

Racing Terms: Glossary for Newer Sailors
If you didn’t grow up sailing, how long did it take you to figure out what sailors mean when they say “put the bow down?” After hearing from newer sailors that the language of racing is hard to decipher, we decided to create a glossary of racing terms and phrases.
We chose racing terms and phrases that are likely to be obscure to newer sailors. To keep the list manageable, we did not include basic sailing terms, words defined in the racing rules, or racing terms applicable to big boats.
Our list is generally organized alphabetically, with a few related terms clustered.
Racing Terms and Phrases for Newer Sailors
| Angle of incidence | The angle between the and the chord line of the sail. | ||
| The direction and speed of the wind as measured from a moving boat. | |||
| Tacking away from other boats to obtain . Often used for starting situations. | |||
| In starting, a boat that sails on starboard tack down towards leeward boats on starboard to try to create room. Barging violates Rule 11 of the Racing Rules of Sailing. | |||
| Flattened | A sail that has been made flatter (less ) with the use of sail controls. | ||
| Starboard blocker | Tactical positioning to windward of a starboard boat. Decreases the chance that a port tack boat will establish a position. | ||
| Kicker, kicking strap (UK term) | Block and tackle (or hydraulic ram on big boats) to control the horizontal angle (rise) of the boom. | ||
| Low mode, foot | Steering away from the wind slightly for more power, | | |
| Sailing downwind with the wind blowing over the leeward side of the boat. | |||
| Depth, fullness | The depth of a sail, measured from the chord line to the deepest point. | ||
| | The chord line of an airfoil is the straight line between the leading and trailing edges | | |
| Strategy to sail from puff to puff while sailing on the as much as possible. | | ||
| Rhumb line | The straight-line course from one mark to the next. | ||
| Layline | Upwind: the line that lets you sail close-hauled to the windward mark (or a start/finish line mark) without pinching. Downwind: the line you would sail to a leeward mark at your optimum angle. | ||
| Long tack/gybe | The tack (or gybe) that lets you sail the most distance without getting to the . Sail the long tack first is a strategy rule of thumb. | ||
| Overstood | A boat that has sailed past the and thus sails extra distance to the mark. | ||
| Loose cover, tight cover | Tactical positioning to stay between your opponents and the next mark. | ||
| Sail control to tension the leading edge ( of the sail. Sometimes incorrectly called downhaul. | |||
| Tack and duck | Maneuver to escape being by a boat close to windward, by bearing off to create separation, then tacking and ducking. | ||
| Draft forward/aft | The point of maximum depth of a sail, measured in percentage of distance from the leading edge. | ||
| Basic puff response technique. | |||
| | The profile of the leading edge of the sail, either flat or rounded. | ||
| Line bias | Starting line: the end of the line that is further upwind. Finish line: the end of the line that is further downwind on an upwind finish. | ||
| Advantaged side | The side of the course that gets you to the next mark faster, due to more wind, favorable shifts, less current, smaller waves, etc. | ||
| Allowing boat to head slightly closer to the wind during a puff. This is an additional component to the technique | |||
| Laying | A boat that is sailing on the toward a mark. | ||
| Bow down, low mode | Sailing upwind at a heading slightly further off the wind than . |
| Make or lose gauge, making or losing trees | A measure of gain or loss against another boat. With a hand-held compass, the change in the compass bearing from one boat to another over time. Without a compass, gains or losses can be measured by the change in the angle between the boats to a distant shore reference, such as trees. | ||
| Shore effects | Wind shifts due to geographic features, such as nearby shore, points of land, obstacles. | ||
| Helm balance, weather helm, neutral helm, lee helm | Helm refers to the tiller. Helm balance refers to the pressure felt on the tiller when sailing in a straight line. Helm balance is often shortened to , as in weather helm, lee helm, neutral helm. | ||
| No-go zone | Boat is stopped or moving slowly heading into the wind (the “no-go zone”). | | |
| Keep it on the wind, point | Sailing close-hauled with the sail trimmed in and the heading such that the sail is neither or . | ||
| Concept that upwind progress can be visualized as a series of lines (ladder rungs) perpendicular to the direction. Also applies downwind. | |||
| Clear lane | A path you can sail on one tack (either upwind or downwind) without encountering other boats or disturbed air. | ||
| Safe leeward position | Sailing upwind with a boat positioned just behind and to windward. The boat ahead and to leeward is advantaged, since the windward boat is not in clear air. | ||
| | The profile of the trailing edge of sail, either flat, open, or closed. | ||
| Distance or angle a boat drifts off course due to the sideways force of the wind. | |||
| A boat that is laterally separated from other boats is said to have , and will gain the most from a favorable shift, but lose the most from an unfavorable shift. | |||
| A wind shift that allows you to change heading without changing sail trim. Upwind, a lift lets you sail closer to the windward mark and a header (knock) makes you sail further away from the mark. Downwind, a lift makes you sail further from the mark and a header (knock) lets you sail closer to the mark. | |||
| Transit | An aid to judging distance to the starting line, by finding a shore reference that aligns with an end of the line. | ||
| Backwind, bubbling | 1) The leading edge of a sail 2) Heading up toward the wind (luffing up) 3) The bubbling or fluttering of a sail when sailing too close to the wind. | ||
| A less skilled sailor. Some experts advise starting next to a marshmallow. | |||
| Bending the mast from a straight line, either fore and aft or laterally. Mast bend is used to shape the sail. | |||
| Rake forward/aft | The fore or aft angle of the mast compared to a horizontal reference. Often measured by the distance from the tip of the mast to the transom. Mast rake affects steering balance and sail power. |
| Sail control to tension the foot of the sail. | |||
| Sailing close to windward of a boat to prevent it from tacking. | |||
| High mode | Sailing upwind at a heading closer to the wind than . | ||
| Velocity | Slang term for velocity. | ||
| Standing rigging, running rigging, shrouds, stays, sheets | |||
| Using weight to roll the boat, minimizing rudder use and accelerating after the sail crosses. | |||
| Strategy to sail in wind that is undisturbed by other boats. | |||
| Angle of heel | Sailing with the optimum angle of heel. The design of the boat (its “lines”) dictates the optimum heel angle. | ||
| Strategy to minimize distance sailed downwind by staying on the gybe that points you closer to the mark. | |||
| In phase, out of phase | Strategy to minimize distance sailed upwind by staying on the tack that points you closer to the mark. If you sail the lifted tack and change tacks when the opposite tack becomes lifted, you are in phase with the shifts. | ||
| Wind that is shifting back and forth around an average direction. | |||
| Wind that shifts in one direction, either progressively, or one time during a leg. | |||
| Unbalanced legs | A course in which the is significantly longer than the opposite tack. A skewed course is not square to the wind. | ||
| A boat on starboard tack (S) crosses just ahead of a port tacker (P) and then tacks as P is ducking her. If S does this right, she will end up with control, to windward and slightly ahead of P. | |||
| Symmetric, asymmetric, code ratings, sheet, guy, pole, dousing | |||
| Separation of air flow from the leeward side of a sail. Also, separation of water flow from a foil (centerboard, lee board, rudder). Stalling occurs when the angle of attack of the sail or foil is too large for the flow velocity. | |||
| When sailing close-hauled, the angle between the boat’s headings on port and starboard tack. Normally roughly 90 degrees but changes by +/- 10 or more degrees in light and heavy wind. | |||
| Tactical maneuver to tack away from a boat ahead and then tack back to obtain clear air or more wind. | |||
| | Sail more closely to the wind, as a result of extra speed. Not exactly the same as , which is sailing closer to the wind but accepting a small loss in speed. | | |
| Shroud tales, luff tales, leech tales | Shroud telltales – ribbons or yarn placed on the side stays (shrouds) to indicate the Luff telltales (or sail tales, woolies, ticklers) – ribbons or yarn placed behind the of the sail to indicate airflow over the sail. Leech tales – ribbons placed on the trailing edge (leech) of the sail to indicate air flow. | Shroud tales Luff tales Leech tales | |
| Expression to help new sailors sail . Move the tiller toward the that are fluttering. | |||
| Control to change the sheeting angle of the mainsheet. | |||
| The direction and speed of the wind over the water, as measured from a stationary reference. | |||
| Twisted, untwisted | The change in from top to bottom of a sail. | ||
| Soak low, heat it up | Downwind technique to maintain boat speed and maximize downwind . Head up in a lull (heat it up) and head down in a puff (soak low). |
| Tensioning the vang so that the boom moves to leeward but not up when easing the mainsheet in a puff. | |||
| Wind shift, righty, lefty | Veer – a shift to the right when facing upwind. Back – a shift to the left when facing upwind. | ||
| VMG | Measure of the rate at which you are making progress directly upwind or downwind. | ||
| Velocity header/lift | A change in the direction due to an increase or decrease in the velocity (not direction) of the . | ||
| Sailing at the heading that maximizes the , upwind or downwind. | |||
| Let the sail breathe, ventilate | Expression that reminds us to avoid over-trimming the sail. Applies in light air, in a lull, or when the boat is going slower than it should for the wind speed. | ||
| Wind vane, wind finder | Rotating wind indicator at the top of the mast. |
Related Content
Sailing Terms from L-36.com – comprehensive list of terms, not limited to racing terms Nautical Language – Expressions from Our Seafaring Roots – not limited to racing terms
Related Posts

Sailing Terms from L-36.com

Nautical Language: Expressions from Our Seafaring Roots
2 thoughts on “racing terms: glossary for newer sailors”.
No mention of ‘Banging the corner’?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Racing Terms: Glossary for Newer Sailors
Courtesy of SailZing Editor – Racing Terms: Glossary for Newer Sailors

Racing Terms: Glossary for Newer Sailors | If you didn’t grow up sailing, how long did it take you to figure out what sailors mean when they say “put the bow down?” After hearing from newer sailors that the language of racing is hard to decipher, we decided to create a glossary of racing terms and phrases.
We chose about 80 racing terms and phrases that are likely to be obscure to newer sailors. To keep the list manageable, we did not include basic sailing terms, words defined in the racing rules, or racing terms applicable to big boats.
Our list is organized alphabetically. Italicised words have separate definitions. If in doubt, you can always ask your local expert here .
Racing Terms and Phrases for Newer Sailors
| Angle of incidence | The angle between the and the chord line of the sail. | |
| The direction and speed of the wind as measured from a moving boat. | ||
| Tacking away from other boats to obtain . Often used for starting situations. | ||
| In starting, a boat that sails on starboard tack down towards leeward boats on starboard to try to create room. Barging violates Rule 11 of the Racing Rules of Sailing. | ||
| Flattened | A sail that has been made flatter (less ) with the use of sail controls. | |
| Starboard blocker | Tactical positioning to windward of a starboard boat. Decreases the chance that a port tack boat will establish a position. | |
| Kicker, kicking strap (UK term) | Block and tackle (or hydraulic ram on big boats) to control the horizontal angle (rise) of the boom. | |
| Sailing downwind with the wind blowing over the leeward side of the boat. | ||
| Depth, fullness | The depth of a sail, measured from the chord line to the deepest point. | |
| Strategy to sail from puff to puff while sailing on the as much as possible. | ||
| Loose cover, tight cover | Tactical positioning to stay between your opponents and the next mark. | |
| Sail control to tension the leading edge ( of the sail. Sometimes incorrectly called downhaul. | ||
| Tack and duck | Maneuver to escape being by a boat close to windward, by bearing off to create separation, then tacking and ducking. | |
| Draft forward/aft | The point of maximum depth of a sail, measured in percentage of distance from the leading edge.. | |
| Basic puff response technique. | ||
| The profile of the leading edge of the sail, either flat or rounded. | ||
| Line bias | Starting line: the end of the line that is further upwind. Finish line: the end of the line that is further downwind on an upwind finish. | |
| Advantaged side | The side of the course that gets you to the next mark faster, due to more wind, favorable shifts, less current, smaller waves, etc. | |
| Allowing boat to head slightly closer to the wind during a puff. This is an additional component to the technique | ||
| Laying | A boat that is sailing on the toward a mark. | |
| Bow down, low mode | Sailing upwind at a heading slightly further off the wind than . | |
| Make or lose gauge, making or losing trees | A measure of gain or loss against another boat. With a hand-held compass, the change in the compass bearing from one boat to another over time. Without a compass, gains or losses can be measured by the change in the angle between the boats to a distant shore reference, such as trees. | |
| Shore effects | Wind shifts due to geographic features, such as nearby shore, points of land, obstacles. | |
| Helm balance, weather helm, neutral helm, lee helm | Helm refers to the tiller. Helm balance refers to the pressure felt on the tiller when sailing in a straight line. Helm balance is often shortened to , as in weather helm, lee helm, neutral helm. | |
| Keep it on the wind, point | Sailing close-hauled with the sail trimmed in and the heading such that the sail is neither or . | |
| Concept that upwind progress can be visualized as a series of lines (ladder rungs) perpendicular to the direction. Also applies downwind. | ||
| Clear lane | A path you can sail on one tack (either upwind or downwind) without encountering other boats or disturbed air. | |
| Layline | Upwind: the line that lets you sail close-hauled to the windward mark (or a start/finish line mark) without pinching. Downwind: the line you would sail to a leeward mark at your optimum angle. | |
| Safe leeward position | Sailing upwind with a boat positioned just behind and to windward. The boat ahead and to leeward is advantaged, since the windward boat is not in clear air. | |
| Distance or angle a boat drifts off course due to the sideways force of the wind. | ||
| A boat that is laterally separated from other boats is said to have , and will gain the most from a favorable shift, but lose the most from an unfavorable shift. | ||
| The profile of the trailing edge of sail, either flat, open, or closed | ||
| A wind shift that allows you to change heading without changing sail trim. Upwind, a lift lets you sail closer to the windward mark and a header (knock) makes you sail further away from the mark. Downwind, a lift makes you sail further from the mark and a header (knock) lets you sail closer to the mark. | ||
| Transit | An aid to judging distance to the starting line, by finding a shore reference that aligns with an end of the line. | |
| The tack (or gybe) that lets you sail the most distance without getting to the . Sail the long tack first is a strategy rule of thumb. | ||
| Backwind, bubbling | 1) The leading edge of a sail 2) Heading up toward the wind (luffing up) 3) The bubbling or fluttering of a sail when sailing too close to the wind. | |
| A less skilled sailor. Some experts advise starting next to a marshmallow. | ||
| Bending the mast from a straight line, either fore and aft or laterally. Mast bend is used to shape the sail. | ||
| Rake forward/aft | The fore or aft angle of the mast compared to a horizontal reference. Often measured by the distance from the tip of the mast to the transom. Mast rake affects steering balance and sail power. | |
| Wind that is shifting back and forth around an average direction. | ||
| Sail control to tension the foot of the sail. | ||
| A boat that has sailed past the and thus sails extra distance to the mark. | ||
| Wind that shifts in one direction, either progressively, or one time during a leg. | ||
| Sailing close to windward of a boat to prevent it from tacking. | ||
| High mode | Sailing upwind at a heading closer to the wind than . | |
| Velocity | Slang term for velocity. | |
| (Not “rum” line) | The straight-line course from one mark to the next. | |
| Using weight to roll the boat, minimizing rudder use and accelerating after the sail crosses. | ||
| Strategy to sail in wind that is undisturbed by other boats. | ||
| Angle of heel | Sailing with the optimum angle of heel. The design of the boat (its “lines”) dictates the optimum heel angle. | |
| Strategy to minimize distance sailed downwind by staying on the gybe that points you closer to the mark. | ||
| In phase, out of phase | Strategy to minimize distance sailed upwind by staying on the tack that points you closer to the mark. If you sail the lifted tack and change tacks when the opposite tack becomes lifted, you are in phase with the shifts. | |
| Unbalanced legs | A course in which the is significantly longer than the opposite tack. A skewed course is not square to the wind. | |
| A boat on starboard tack (S) crosses just ahead of a port tacker (P) and then tacks as P is ducking her. If S does this right, she will end up with control, to windward and slightly ahead of P. | ||
| Separation of air flow from the leeward side of a sail. Also, separation of water flow from a foil (centerboard, lee board, rudder). Stalling occurs when the angle of attack of the sail or foil is too large for the flow velocity. | ||
| When sailing close-hauled, the angle between the boat’s headings on port and starboard tack. Normally roughly 90 degrees but changes by +/- 10 or more degrees in light and heavy wind. | ||
| Tactical maneuver to tack away from a boat ahead and then tack back to obtain clear air or more wind. | ||
| Shroud tales, luff tales, leech tales | Shroud telltales – ribbons or yarn placed on the side stays (shrouds) to indicate the Luff telltales (or sail tales, woolies, ticklers) – ribbons or yarn placed behind the of the sail to indicate airflow over the sail. Leech tales – ribbons placed on the trailing edge (leech) of the sail to indicate air flow. | |
| Expression to help new sailors sail . Move the tiller toward the that are fluttering. | ||
| Control to change the sheeting angle of the mainsheet. | ||
| The direction and speed of the wind over the water, as measured from a stationary reference. | ||
| Twisted, untwisted | The change in from top to bottom of a sail. | |
| Soak low, heat it up | Downwind technique to maintain boat speed and maximize downwind . Head up in a lull (heat it up) and head down in a puff (soak low). | |
| Tensioning the vang so that the boom moves to leeward but not up when easing the mainsheet in a puff. | ||
| Wind shift, righty, lefty | Veer – a shift to the right when facing upwind. Back – a shift to the left when facing upwind. | |
| VMG | Measure of the rate at which you are making progress directly upwind or downwind. | |
| Velocity header/lift | A change in the direction due to an increase or decrease in the velocity (not direction) of the . | |
| Sailing at the heading that maximizes the , upwind or downwind. | ||
| Let the sail breathe, ventilate | Expression that reminds us to avoid over-trimming the sail. Applies in light air, in a lull, or when the boat is going slower than it should for the wind speed. . | |
| Wind vane, wind finder | Rotating wind indicator at the top of the mast. |
ABOUT DOYLE SAILS // As sailors, our obsession with sailing connects us to the water. The water is our playground, a sanctuary where we seek enjoyment, a competitive playing field where we race; it’s sometimes our home and always a place that unlocks our sense of adventure wherever that adventure might take us.
Our obsession with sailing takes us to every corner of the world and onboard every yacht. We become part of teams, share in the adventures of friends and families, sharing our knowledge and experience with those who have the same passion for sailing as we do. Sailing is in our DNA, where the water unlocks our sense of adventure. We are the custodians of a legacy that has been supporting sailors for close to four decades, and while our world changes around us, our commitment to sailors who seek the same enjoyment and adventure as we do hasn’t.
From our sailors to yours, we are your experts in sailing. Your adventure starts with Doyle. By sailors, for sailors.
- America’s Cup Updates
- Southampton Boat Show
- British Yachting Awards
- Print Subscription
- Digital Subscription
- Single Issues
Your special offer

The A-Z of essential sailing terms

You may not be super confident in a boat yet but with our guide to sailing jargon you’ll sound it in no time .
Essential sailing terms.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

Scottish Marina Celebrates 40 Years: Largs Yacht Haven

Chartering in Greece: Three Greecy Areas

RNLI named as the Official Charity for Round the Island Race 2024

Yachts & Yachting is the leading performance sailing magazine, covering every aspect of the racing scene, from dinghies to keelboats. Our insightful features and stunning photography bring you the inside track on the world’s most exciting regattas together with advice and inspiration from the very best sailors, coaches and industry experts.
- News & Events
- Sailing Techniques
- Event Spotlight

ADVERTISING

© 2024 Chelsea Magazine Company, part of the Telegraph Media Group | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy

Published on September 5th, 2021 | by Editor
Racing Terms: Glossary for newer sailors
Published on September 5th, 2021 by Editor -->
If you didn’t grow up sailing, how long did it take you to figure out what sailors mean when they say “put the bow down?” After hearing from newer sailors that the language of racing is hard to decipher, SailZing created a glossary of racing terms and phrases. Here’s a sample:
• Bail out: Tacking away from other boats to obtain clear air. Often used for starting situations. • In the groove: Sailing close-hauled with the sail trimmed in and the heading such that the sail is neither luffing nor stalling. • Marshmallow: A less skilled sailor. Some experts advise starting next to a marshmallow. • Skewed course: A course in which the long tack is significantly longer than the opposite tack. A skewed course is not square to the wind. • Tiller towards trouble: Expression to help new sailors sail in the groove. Move the tiller toward the luff telltales that are fluttering.
For the full list, click here .

Tags: education , SailZing
Related Posts

Devil in the Details: Life Jackets →

Patience has its place on the racecourse →

Tips to winning a protest →

Improve your weeknight race results →
© 2024 Scuttlebutt Sailing News. Inbox Communications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. made by VSSL Agency .
- Privacy Statement
- Advertise With Us
Get Your Sailing News Fix!
Your download by email.
- Your Name...
- Your Email... *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Confused by the terminology? Our sailing glossary has all you need to know to keep up with the state of play
While sailing is exciting for its fans, its hyper-specific nautical terms, regatta norms and general rules can be confusing for a novice to understand. In a bid to clear the muddied waters, we have thrown together something of a cheat sheet for anyone who wants to deepen their knowledge.
THE TERMS ‘Stuffing It’ or ‘Splash Down’ This is when the boat drops off the foils and the hulls hit the water, usually in a very dramatic fashion that soaks the sailors.

‘Velocity Made Good’ (VMG) A term used in yacht racing to indicate the speed of a sailboat towards (or from) the direction of the wind.
‘Fly Time’ The amount of time the boat spends foiling. The ideal situation would be for a team to make it around the entire course with 100 percent fly time, which means their hull never touches the water.
‘Wingwash’ When sailboats sail close to each other, one can affect the other’s quality of wind. The result of this change is sometimes called “wingwash.”
‘One & In’ This term is used to describe a boat that only needs to make one more tack/jibe to make the next mark .
‘Split & Cover’ As the boats approach the top or bottom marks, they must decide how to navigate them. If they choose the same mark, it’s referred to as a ‘cover,’ and if they go in opposite directions, it’s a ‘split.’
‘Dialling Down’ A strategic move that often arises in crossing situations, this is when one boat tries to force the other further downwind in an attempt to throw them off course.
‘Dialing Up’ Something that typically comes up around the start of a race, this is when one boat will attempt to force the other upwind.
‘Squall’ Referring to a strong and sudden rise in wind that usually lasts a few minutes, this phenomenon can make sailing conditions particularly challenging.
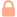
Bonus: How to Tie a Cleat Hitch in 3 Simple Steps The cleat hitch is a simple knot to master and is usually used for securing boats to a dock. It ties and unties quickly and neatly and will be the easiest way to impress your friends next time you’re out on the water.
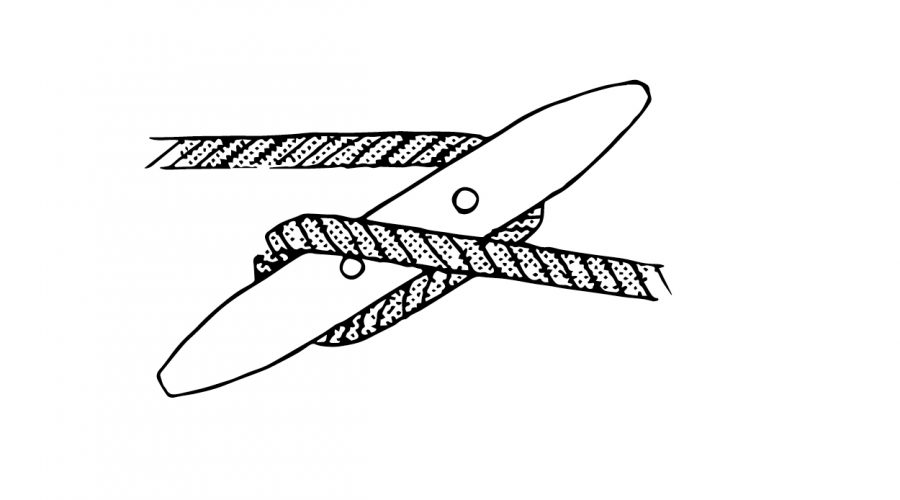
1. Bring the rope under the far side of the cleat, then around and under the opposite horn.
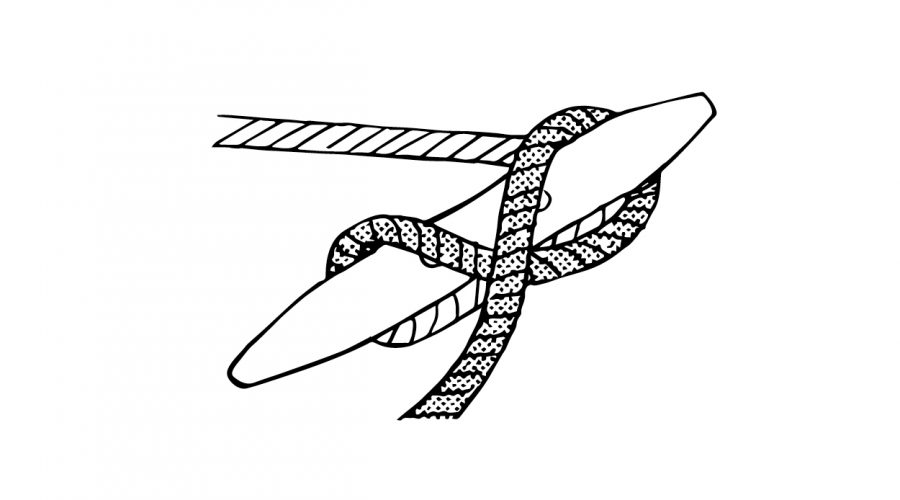
2. Go over the middle of the cleat and make a figure 8 around the two horns.
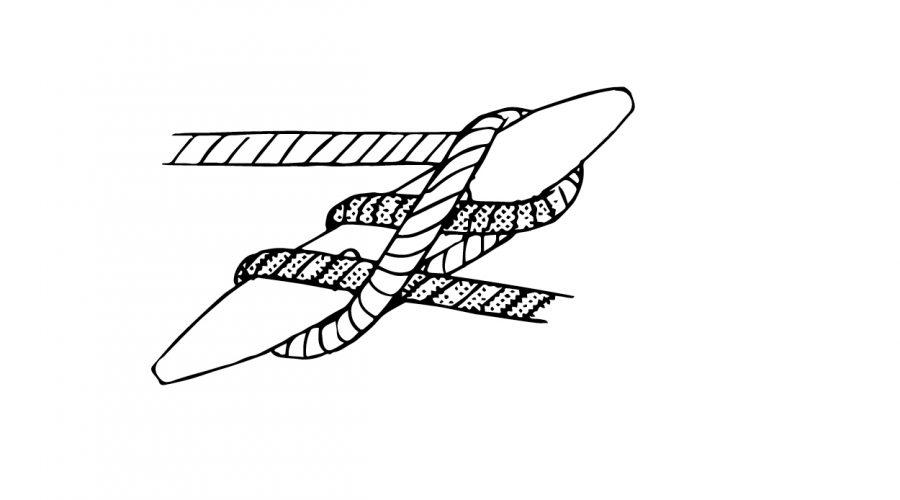
3. Make a small loop in the rope, then turn it over (to the left) in your hand and loop over the bottom horn of the cleat. Pull tight.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE
29 Feb 2024

Pick up some late summer outdoor furniture deals in these epic designer sales
Sailing regatta.

Sail in style with these boat-day essentials that will have you looking undeniably dapper

Etiquette 101: How to apply sunscreen to someone you don’t know well

Avoid being a bore on-board and follow these simple rules for securing your status as a truly interesting guest
More sailing regatta stories →, connect with us.

CURRENT ISSUE
Gastronomy, style, culture, design, wellbeing, travel..
For more exclusive access to what the city has to offer, engaging content, excellent imagery and thought provoking commentary on the life that surrounds you, subscribe to Denizen magazine now.
Sign up to the Denizen Weekly
Get the latest and greatest happenings in Auckland delivered straight to your inbox every Wednesday morning.
Interested in Advertising?
Kindly share a little more insight into who you are below and one of our team will be in touch soon.
Aft : The rear of a boat, close to the stern Backstay : A mast support that runs from the top of the mast to the stern of the boat. It may be adjustable in order to bend the mast backward or to increase tension on the forestay tool Ballast : Weight in the keel of a boat that adds stability Beam : A boat's greatest width Beating : Sailing (or pointing) at an angle into the wind or upwind. Since sailboats cannot sail directly into the wind, "beating" is the closest course to the wind they can sail. Bilge : The lowest part of a boat's hull
Blanketing : A tactical maneuver in which one boat slows a competitor by positioning itself to obstruct the competitor's wind Block : An assemblage of one or more sheaves (pulleys) housed in a plastic or metal case that changes the direction of travel of a line (rope) and may be attached to a boat's deck, spar or other stationary object Boom : Spar to which a sail's lower edge or foot is attached. The boom is attached to the mast at the gooseneck. Boom vang : Lines that control the boom. These lines run from the boom to the base of the mast and are used when reaching and running. Bow : The front of the boat Broach : When in a downwind situation, the boat turns uncontrollably and is pushed by the wind onto its side, lying with the mast parallel to the water. As a rule, the boat will right itself. Buoy : A floating marker Cam cleat : A mechanical cleat used to hold a line automatically. It uses two spring-loaded cams that come together to clamp their teeth on the line, which is placed between them. Also known as jam cleat . Centerboard : Like a keel, it is a weighted appendage projecting below the boat that keeps it from capsizing and also supplies the hydrodynamic lateral force that enables the boat to sail upwind. Unlike a keel, it is retractable. Cleat : A fitting, typically with projecting ends, that holds a line against the tension from the sails, rigging or mooring Clew : The lower corner of a mainsail or jib and either lower corner of a spinnaker Coming about : Turning the boat so the bow crosses through the eye of the wind, thereby changing the side of the yacht on which the sails are carried. Also known as tacking. Covering : A tactical maneuver in which a boat stays between a competitor and the wind or the next mark Daggerboard : An adjustable fin primarily used to stop the boat moving sideways through the water. Also known as centerboard. Dinghy : The Laser, Laser Radial, 470, and Finn are all dinghies that have been used in Olympic sailing - they all have one hull and a centreboard or daggerboard Downwind : The point of sail when the wind blows from aft of the boat's beam Drag : The negative or retarding force acting on a body, such as a boat moving through a fluid parallel and opposite to the direction of motion Fall off : A maneuver in which a boat turns away from the wind Fleet racing: Competition format were entries race against each other around a course Foot : The bottom edge of a sail Genoa/Headsail/Jib : The smaller sail set in front of the mast Gooseneck : A fitting that attaches the boom to the mast Gybe : Turning the boat so the stern crosses through the eye of the wind, (thereby changing the side of the boat on which the sails are carried (opposite of tacking). Also spelled jibe. Halyard : A line used to hoist and hold up a sail Header : Wind shift that causes the boat to head away from the mark Helmsman : The crew member who steers the boat; also the skipper, or the "driver" Hiking out : Leaning out of the craft in order to change the center of gravity in the boat and go faster Hiking straps : Straps attached to the feet that help a sailor hike out more, minimizing the chance of falling out of the boat Hull: The main body or shell of a ship or other vessel, including the bottom, sides, and deck ISAF : International Sailing Federation, the world governing body of sailboat racing Jam cleat : A device used to grip a line (rope). It has two rows of V-shaped molded teeth that grip the line when it is jammed in the groove. Also known as cam cleat. Jib : A foresail that overlaps the shroud base and is used for sailing upwind Jibe : Same as the gybe -- turning the boat so the stern crosses through the eye of the wind, thereby changing the side of the yacht on which the sails are carried (opposite of tacking) Kee l: A weighted, non-moveable appendage projecting below the boat that keeps it from capsizing and also supplies the hydrodynamic lateral force that enables the boat to sail upwind Kite : Large, light ballooning sails that are only attached to the mast at the corners. They are used when sailing downwind. Also known as spinnaker . Knot : One nautical mile per hour Lay : To sail a course that clears an object or racecourse marker buoy such as the windward and leeward marks. When a boat is doing so, it is said to be "laying the mark." Layline : An imaginary line projecting at an angle and corresponding to the wind direction from either side of a racecourse marker buoy that defines the optimum sailing angle for a boat to fetch the mark or the finish line. When a boat reaches this point, it is said to be "on the layline." Going beyond the layline means the boat is sailing a greater distance to reach the mark or finish line. Leech : The trailing edge of a sail or the curve of a sail Leeward : The side furthest away from the wind Lines : A nautical term for ropes Luff, to : Bubbling or flapping of a sail when it is not trimmed enough or is being back winded by another sailor when the course sailed is too close to the wind Mainsail : The sail behind the mast Mark : A buoy used in a racecourse Mast : The vertical spar that holds up the sails Match racing : A racing format in which only two boats compete at a time, as opposed to fleet racing, wherein three or more boats sail at once Medal race : The final race in the series. Only the top-10 boats after the opening series compete and scores are doubled. Multihull : Nacra 17 (boat used in its inaugural event at the 2016 Rio Olympic Games) - A boat with more than one hull. A boat with two hulls is also known as a catamaran and a boat with three hulls is knows as a trimaran. Nautical mile : The unit of geographical distance used on saltwater charts; one nautical mile equals 6,076 feet or 1.15 statute miles. Therefore, one statute mile equals 0.87 of a nautical mile. Off the wind : Sailing away from the wind; also downwind, reaching or running Plane : A boat planes when it sails over her own bow wave so only a small section of the hull is in the water. This allows the boat to go faster than the theoretical maximum hull speed. Pointing : Sailing at an angle into the wind or upwind. Depending on a boat's design, some will "point higher" or sail more directly into the wind and thus sail a shorter course to a given mark on the racecourse. Port : Nautical term for the left side of a boat when facing forward Port tack : Sailing with the wind blowing onto the port side and the mainsail on the starboard side Race officials : The officials responsible for running the race and enforcing the rules. This group includes the measurers who ensure that each sailor's equipment is equal and within the rules, the race officers who run the races and the judges and umpires who are rules experts and make decisions about whether rules have been broken. Reef : To decrease a sail's size Rigging : The wires, lines, halyards and other items used to attach the sails and the spars to the boat. The lines that do not have to be adjusted often are known as standing rigging. The lines that are adjusted to raise, lower and trim the sails are known as running rigging. Rudder : A moveable fin located underneath the back of the boat that steers the craft Running rigging : All moving rods and lines that support and control the mast and sails Shackle : A metal connector that attaches to other fittings with the use of a pin that is inserted through the arms of a U Sheet : A line that controls sails Skiff : 49er - A light open dinghy with a self-draining hull Slalom finish : A technical section of the windsurfing (RS:X) course involving multiple changes of direction in quick succession Spar : A basic term for a mast, boom or yard Spinnaker : Large, light ballooning sails that are only attached to the spars at the corners. They are used when running or reaching, sailing downwind. Starboard : Nautical term for the right half of the boat when facing forward Starboard tack : Sailing with the wind blowing onto the starboard side and the mainsail on the port side Stern : The rear of the boat Tacking : Turning the boat so the bow crosses through the eye of the wind, thereby changing the side of the boat on which the sails are carried (opposite of gybing) Tiller : A lever used to turn the rudder of a boat from side to side Trapeze : To stand on the side of the boat to maximize the effect of the body weight Trim : To adjust the sail to the right shape and angle to the wind. The process of "hiking out," or changing the center of gravity of the boat in order to go faster. Upwind : Toward the direction from which the wind blows; windward. Way : Forward motion of a boat. A term typically used in the context of saying that a boat is making way, is underway, or has way on. Windward : The side closest to the wind
Start your Olympic journey today on SportsEnginePlay.com , the Home of Youth Sports™
Note: Some components of NBCOlympics.com may not be optimized for users browsing with Internet Explorer 11, 10 or older browsers or systems.
30 Must-Know Sailing Terms, Phrases and Slang
June 9, 2024
We are reader-supported. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more.

Set sail on an epic adventure across the high seas with language as your compass!
From the salty whispers of old seadogs to the crisp commands on a racing skiff, mastering these 30 essential sailing terms will transform you from a landlubber to a savvy sailor.
Hoist the sails and let’s navigate the nautical jargon together!
Must-Know Sailing Terms, Phrases and Slang:
- Gybe (jibe)

Table of Contents
#7 Gybe (jibe)
#12 leeward, #16 sail trim, #17 starboard, #20 telltale, #21 windward, #28 mainsail, #29 spinnaker, what are some sailing terms for beginners, what are some funny sailing terms, what is a famous sailing phrase.
The aft refers to the back of the boat or nearer to the stern. Sailors often say “move aft” when directing someone towards the rear end of the vessel, an essential term for orientation on board.
The beam of a boat is its widest part and is a critical dimension for stability. When winds blow from the side, they hit the beam, making an understanding of this term important for handling the vessel.
The bow is the front end of a sailing vessel. When facing forward, sailors will refer to things in front of the boat or point out objects by saying “off the bow.”
To capsize is to overturn in the water, causing the boat to flip onto its side or completely upside down. This term is crucial for safety discussions and is one sailors hope they rarely have to use.
The deck is the surface area on top of the boat that crew can walk on. It’s where the majority of sailing activity takes place and where equipment like winches and cleats are mounted.
To furl a sail is to roll or fold it up neatly, usually to reduce its surface area in strong winds or when not in use. Proper sail furling is essential for sail management and longevity.
A maneuver used to change the direction of a sailboat by turning the stern through the wind. This contrasts with tacking, where the bow moves through the wind. Gybing is often used when sailing downwind and requires careful handling to prevent the boom from swinging dangerously across the boat.
A line or rope used to hoist (raise) or lower sails on a boat. Each sail typically has its own halyard which is attached to the head of the sail; pulling on the halyard raises the sail up the mast to catch the wind.
The helm is the wheel or tiller used to steer a boat. Standing at the helm, a sailor has control over the vessel’s direction, playing a critical role in navigation and maneuvering.
A jib is a triangular sail set forward of the main mast, generally used to increase speed and manageability. Sailors adjust the jib to optimize boat performance in various wind conditions.
The keel is a structural component extending along the bottom of a boat’s hull, from bow to stern, providing stability and minimizing sideways drift. It’s crucial for balance and can house ballast to keep the vessel upright.
Leeward, or the lee side, refers to the side of a boat sheltered from the wind. Sailors often use this term to describe the direction downwind or an area with lesser wind pressure.
The mast is a tall, vertical pole on a ship that supports the sails and rigging. It’s a critical component for sailboats, as it serves as the focal point for sail attachment and wind harnessing.
Port denotes the left side of a boat when facing the bow. A mnemonic to remember is “port” and “left” both of which have four letters. It’s also marked with a red light at night.
A flat piece, usually made of wood, fiberglass, or metal, located beneath the boat that is used to steer. The rudder is controlled by the helm (steering wheel or tiller), allowing the skipper to guide the boat’s direction through the water.
The art of adjusting the position and shape of the sails in response to wind conditions and desired boat speed or direction. Proper sail trim optimizes the boat’s performance and efficiency, making it a crucial skill for effective sailing.
Refers to the right-hand side of a boat when facing forward toward the bow. Sailors need to remember “port” is left, “starboard” is right, crucial for navigation and obeying the rules of the water.
The back or aft-most part of a vessel, opposite of the bow. From the stern, sailors control steering and often find the propulsion system, essential for maneuvering and power management on the water.
In sailing, to tack is to turn the boat’s bow through the wind to change direction, also the lower corner of a sail. Skilled tacking is fundamental for making headway against the wind and requires precise crew coordination.
Strips of fabric or yarn attached to sails or rigging that indicate wind direction relative to the boat. Observing telltales helps sailors optimize sail trim and boat positioning for maximum efficiency.
The direction from which the wind is blowing, the opposite of leeward. Sailors often need to keep track of the windward side for strategic positioning, especially during racing or in crowded waters.
A two-masted sailing craft with the mizzenmast (the smaller second mast) positioned behind the rudder post. The yawl rig is favored for cruising due to its balance and ease of handling in various wind conditions.
The lowest compartment on a ship, below the waterline, where water typically collects and is often pumped out to prevent sinking. The bilge can also refer to the broader internal parts of a hull.
A horizontal pole that extends from the bottom of a mast, used to secure the bottom of a sail. It swings from side to side, and caution is needed to avoid it during maneuvers like tacking or gybing.
A device fixed to the deck or mast used to secure rope ends. Cleats can be horned, cam, or clam in shape, and are essential for holding lines in place, especially when mooring or adjusting sail trim.
The area where boats are parked, tied, and secured to a pier or wharf. Docks provide access to land for loading and unloading, as well as a place for maintenance and repair.
A unit of speed in nautical terms, equivalent to one nautical mile per hour. The term also refers to the tying of ropes in various configurations for securing and rigging purposes.
The primary and usually the largest sail on a typical sailboat, hoisted on the mainmast. It provides the main driving force for the sailboat and is manipulated for steering and speed control.
A spinnaker is a large, lightweight sail designed for sailing downwind or on a reaching course when the wind comes from behind the boat. When deployed, it fills with wind and balloons out in front of the boat, significantly boosting speed. Widely used in racing for its effective wind harnessing, spinnakers come in various shapes and sizes tailored to different sailing conditions and boat types.
A mechanical device on a boat used to handle heavy loads, such as tightening the ropes (sheets) that control the sails. Winches provide mechanical advantage, making it easier to pull in or let out sails, especially under strong wind conditions. They are essential for managing larger sails and conducting precise adjustments.

“Aft,” “Bow,” “Stern,” and “Mainsail” are some sailing terms beginners should start with. These basic terms help novices understand directions and parts of the boat.
“Boom,” “Jib,” and “Bilge” are some funny sailing terms that can sound amusing outside the sailing context, bringing a lighter side to nautical vocabulary.
“Three sheets to the wind” is a famous sailing phrase, historically referring to a ship with its sheets (lines controlling the sails) flapping loosely in the wind, implying that the vessel is out of control, often used today to describe someone who is inebriated.
Meet Rev, one of our dedicated team members who embodies the essence of sports passion. When he’s not immersed in the world of sports content creation, Rev is busy honing his skills in esports and exploring the great outdoors through activities like hiking and basketball.
Related Posts

Top 11 Best Brands for Sailing in the World
Craving the thrill of the open seas? Navigate in style and confidence with gear from the world’s elite sailing brands….

Who Invented Sailing?
Sailing was invented by ancient civilizations thousands of years ago. It has since evolved into a popular sport and mode…

11 Countries Where Sailing is Most Popular (Ranked)
Ahoy, young adventurers! Set sail on an epic quest to discover the shores that embrace sailing like no other. Ready…
- Newsletter (free downloads)
- YouTube (420k+ views)
- Pinterest (111k+ monthly views)
- Instagram (5 Reels a Week)
- TikTok (5 Videos a Week)
- ❄️ Winter & Ice Sports
- ⚽ Ball Sports
- 🥊 Combat & Strength Sports
- 🪂 Extreme & Adventure Sports
- 🎯 Precision Sports
- 🏸 Racquet Sports
- 🌊 Watersports
- 🏃♀️ Athletics & Endurance Sports
- Press Releases
- SportColorCodes.com

© Sun Media Brands,
Terms of Use Earnings Disclaimer Privacy Policy
We are reader-supported. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more.

Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained]
True, when you first witness a sailboat race, you might believe it’s too confusing and chaotic (it can be both). But, like with anything new, you may ease into it gradually. This is intended to allow you to take several actions at once.
Racing a sailboat is a lot of fun. It blends the excitement of sailing your own boat with the raw rivalry of trying to beat another boat of comparable size. Racing also teaches you boat handling and sail trim in a manner that cruising cannot: by comparing your speed and handling to those of other boats.
Let us jump into the article to learn more about sailboat racing.
![Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained] 1 Sailing boat with two crew members participating in the sailboat racing](https://maritimepage.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Sailboat-Racing-Rules-and-Classes-2-1024x683.webp)
Basic Insights Into Sailboat Racing
Sailboat racing may be separated into three parts: start , headwind , and tailwind . During a sailboat race, it is important to ensure that the beginning of the race must be strong. The start determines the overall outcome of the race and thus is considered very crucial for the race. It brings great advantage to the competitor and this is often very underrated.
As soon as the countdown is complete, it is necessary to make sure that the competitor has crossed the starting line effectively. Generally, warnings are given at 5mins and subsequently at 4mins and 1min .
Another very important aspect to consider is the path . The competitor must be able to determine a clear path to sail through and the direction of the race course must also be perceived correctly to ensure a favorable outcome. Free lanes enable the competitor with ideal angles to the wind with which they can easily navigate without having to go against disturbed wind or wind shadows from rival boats.
![Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained] 2 Sailboat Racing Rules and Classes - Small sailboat racing](https://maritimepage.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Sailboat-Racing-Rules-and-Classes-Small-sailboat-racing-1024x819.webp)
The Starting Line
Oftentimes, the first leg of the race will be upwind, after the starting line is crossed. At this point again, it is important to note that starting strong is crucial for an upwind race as more free lanes are accessible the further ahead the competitor is in the convoy.
The necessary determinants to be noted and kept in consideration throughout the race for effective upwind sailing strategies are the following factors: wind direction, wind speed, and rivals. But the last aspect can be tricky as everyone’s goal is ultimately to win.
Competitors need to base their choices for sailing downwind on the same findings, but with a few minor variations. Being at the forefront and tagged by rivals can be seen as a mode of suffering when the competitor must keep sailing in the wind shadows of all the boats behind. Here, there’s an advantage to be thought of if the competitor can position themselves at the rear. Any lane can be chosen at proper intervals to make up for the lost ground.
However, usually, down winds result in shorter wins and losses than up winds . This is because there is less transverse separation during down winds when compared to up winds.
![Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained] 3 Sailboat Racing of the same class maneuvering near the start line](https://maritimepage.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Sailboat-Racing-Rules-and-Classes-Dinghy-sailboat-racing-1024x683.webp)
Different Types of Sail Racing Classes
Sailboat racing can be done in different ways. Each race lasts for about 45min to 1hr and is conducted on a course marked by buoys mounted by the racing committee. One can also take part in “ distance races “. In this case, the “ natural ” surroundings will typically provide the race course.
The points of sail during the race depend on the predominant wind direction factors on the day of the race, which is the other major variation besides the length. While racing on the course, the race committee places the buoys in such a manner that the race course is adapted to the wind , this mostly enables the competitors to accurately identify which sail has to be deployed for the upcoming leg .
At the race course and during the distance races, the sailboats that participate are usually of various types and are commonly very diverse. As a result, the organizing committee frequently employs intricate “ handicap ” mechanisms to even out variations across boat types . The system is often country-based and it has been developed based on the most common types of boats in a country. The RC , ORC , and IRC systems are the most widely used on an international scale .
These systems compute a factor that should be multiplied by the exact time required to sail one nautical mile using complex formulas . They are based on the dimensions of the boat’s length, weight, sail size, types, and design of the boat along with the materials used .
To find the adjusted race time that can be used to compare with other competitors, this f actor is multiplied by the amount of time it took you to complete the race and the distance of the race .
It is very necessary to remember that these systems are not entirely accurate and they cannot be completely relied on. They can only be used to a certain extent for performance comparison . Hence it is advised that one must compete in races where the competing boats are similar to accurately assess the racing skills of the competitor.
![Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained] 4 Sailboat Racing Rules and Classes](https://maritimepage.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Sailboat-Racing-Rules-and-Classes-6-1024x683.webp)
Main Rules in Sailboat Racing
These races are administered and authorized by the International Racing Rules of Sailing . It lays down rules and safety measures to sail safely across the race course along with the entire fleet, whose goal is to sail successfully during the race as well.
A rulebook is laid down with fundamental rules providing explanations and specimens about ensuring how to maintain and regulate according to the laws during a variety of circumstances that can arise between competing sailboats during the course of the race.
The most fundamental rule is that vessels with their starboard side windward must give way to vessels with their port side windward . This implies that the port-tack boat must either tack or bear away to pass behind the stern of the starboard-tack boat when two boats on opposite tacks come together . The leeward boat always has the right of way over the windward boat when there are two boats on the same tack.
![Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained] 5 YouTube player](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/y_Au4vEg-Aw/maxresdefault.jpg)
Although this is the case, it is essential to note that the boat with the right of way must always ensure to leave other sailboats adequate space and time to avoid collision and accidents . While trying to maintain contact with other competitors, one must be very safe and secure as a significant level of rule interpretation can be enforced.
Violation of any rule can cause you to self-forfeit from the race . Hence it is advised to make amends and surrender upon having committed a conscious foul. Most admitted fouls are looked over following a penalty turn of 360 degrees or 720 degrees . Sailing instructions can be seen as a guide in all circumstances to find more detailed information about the same. A few rules can also be helpful when it comes to knowing what to be worn during the race apart from obvious determinants like the weather and climate conditions.
![Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained] 6 Sailboat Racing Rules and Classes](https://maritimepage.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Sailboat-Racing-Rules-and-Classes-4-1024x678.webp)
Main Equipment Used In Sailboat Racing
The sport of sailing is generally very physically taxing and hence requires e xtraordinary energy throughout the course of the race especially while rounding marks and sailing downwind.
When the atmospheric temperature falls due to wind-chill effects , it makes much colder winds frequently. In such circumstances, making use of a windproof outer layer will guard against the wind chill and this material is also breathable . Such measures must be ensured to avoid being cold and clammy. Wearing boots can also ensure to keep yourself warm and comfortable.
Looking into the technical aspects , sailboats need to ensure they are fully equipped with communication and navigation devices such as VHF, GPS, Sat Phones , and so on.
![Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained] 7 Sailboat Racing - Volvo Ocean Racing Sailboat](https://maritimepage.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Sailboat-Racing-Volvo-Ocean-Racing-Sailboat-1024x682.webp)
Different Types Of Sailboat Races
Sailboat racing is a diverse and dynamic sport that encompasses a wide range of different race types , each with its own unique rules, tactics, and strategies . Understanding the different types of sailboat races is crucial for sailors looking to compete at a high level and succeed in this exciting sport.
One of the most common types of sailboat racing is fleet racing, which involves a large number of sailboats competing in a single race. In fleet racing, the sailboats start together and sail a predetermined course, with the first boat to cross the finish line being declared the winner. Fleet racing often requires a high degree of tactical maneuvering, as sailors must navigate around other boats and adjust their tactics to account for wind shifts and other factors.
Another popular type of sailboat racing is match racing, which involves two sailboats competing head-to-head in a series of races. In match racing, the emphasis is on tactical maneuvering and outsmarting your opponent, rather than simply being the fastest boat on the course. Match racing typically involves a complex set of rules and regulations governing how boats can interact with each other on the course, and sailors must be highly skilled at reading wind shifts, controlling their boats, and outmaneuvering their opponents.
![Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained] 8 sailboats with black sails](https://maritimepage.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/sailboats-with-black-sails.jpg)
Team racing is another type of sailboat racing that involves multiple sailboats competing against each other in a team format. In team racing, each team consists of multiple boats, and the team with the best overall performance across all of its boats is declared the winner. Team racing often requires a high degree of coordination and strategy, as sailors must work together to achieve a common goal and coordinate their tactics to maximize their chances of success.
In addition to these main types of sailboat racing, there are also a variety of specialized race types that are popular in different parts of the world . For example, ocean racing involves sailing across the open ocean over long distances and requires a high degree of skill and endurance. Inshore racing , on the other hand, takes place in protected bays and harbors and often involves short, fast races with frequent wind shifts and other challenges.
Regardless of the type of sailboat racing, one thing remains constant: the need for skilled and experienced sailors who can navigate their boats through a wide range of conditions and challenges. Whether you’re a seasoned veteran or a beginner just getting started, mastering the different types of sailboat racing can be a highly rewarding and exhilarating experience, and can lead to a lifetime of excitement and adventure on the water.
![Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained] 9 Sailboat Racing Rules and Classes](https://maritimepage.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/Sailboat-Racing-Rules-and-Classes-5-1024x683.webp)
Classes Of Sailboats Commonly Used In Racing
Sailboat racing is a highly competitive and dynamic sport that encompasses a wide range of different classes of sailboats, each with its own unique characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses. Understanding the different classes of sailboats used in racing is crucial for sailors looking to compete at a high level and succeed in this exciting sport.
One of the most common classes of sailboats used in racing is the dinghy , which is a small, lightweight boat typically sailed by one or two people. Dinghies are highly maneuverable and responsive and can be sailed in a wide range of conditions, from light winds to strong breezes. Popular dinghy classes include the Laser , the 420 , and the Optimist , each of which has its own unique rules and specifications.
Keelboats are another popular class of sailboats used in racing, and are typically larger and heavier than dinghies, with a fixed keel that helps to provide stability and control. Keelboats come in a wide range of sizes and designs, from small one-design boats like the J/24 to larger performance-oriented boats like the TP52. Keelboats are often sailed by a crew of several people and require a high degree of coordination and teamwork to sail effectively.
Multihulls are another popular class of sailboats used in racing and are characterized by their multiple hulls providing greater speed and stability than traditional monohull sailboats. Multihulls come in a variety of different designs and sizes, from small catamarans to large trimarans , and are typically sailed by a crew of several people. Multihulls can be highly competitive and exciting to sail, but also require a high degree of skill and experience to handle effectively.
In addition to these main classes of sailboats, there are also a variety of specialized classes that are popular in different parts of the world. For example, in Australia and New Zealand, the 18-foot skiff is a highly competitive and popular class of sailboats, characterized by its large sail area and high speed. In Europe, the Dragon is a classic one-design keelboat that has been popular for decades and is known for its elegant design and excellent performance.
Regardless of the specific class of sailboats used in racing, one thing remains constant : the need for skilled and experienced sailors who can navigate their boats through a wide range of conditions and challenges . Whether you’re racing a dinghy, a keelboat, a multihull, or some other type of sailboat, mastering the unique characteristics and challenges of your boat is key to achieving success on the water.
To become a successful sailboat racer , it’s important to not only master the technical skills needed to sail your boat effectively , but also to develop a deep understanding of the rules, tactics, and strategies that govern sailboat racing . By immersing yourself in the world of sailboat racing and learning from experienced sailors, you can build the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in this exciting and challenging sport.
![Introduction to Sailboat Racing [Rules and Classes Explained] 10 YouTube player](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/sAxD7w0lDhA/maxresdefault.jpg)
In conclusion, participating in a race can be very enjoyable in both cases. The first case is where someone is learning the art of sailing or like in the second case where one could be trying to gain some prior expertise on the sea.
If winning the race is one’s main aim then the key thing to remember is to make sure that you tack at the right moments. To trim the sails to completely catch the wind and last but not least, to communicate well with the rest of the crew.
- Recent Posts
- The Role of Cargo Ships in Global Trade – August 22, 2024
- Report: Yang Ming’s YM Mobility Explosion at Ningbo-Zhoushan Port – August 9, 2024
- Understanding Drillships: Types, Key Features and Advancements – August 1, 2024
About the author
I worked as an officer in the deck department on various types of vessels, including oil and chemical tankers, LPG carriers, and even reefer and TSHD in the early years. Currently employed as Marine Surveyor carrying cargo, draft, bunker, and warranty survey.
Latest posts

The Role of Cargo Ships in Global Trade
Contents show Volume of Goods Transported by Sea Key Global Trade Routes Economic Impact of Maritime Shipping Types of Cargo Commonly Transported Environmental Considerations Conclusion Cargo ships are the lifeline […]

What Are AGVs? Automation Becoming Increasingly Common in Seaports
What are AGVs? Automated guided vehicles can minimize the troubles of manual operations and enhance seaport operations.

Report: Yang Ming’s YM Mobility Explosion at Ningbo-Zhoushan Port
A massive explosion occurred on the container ship YM Mobility while it was berthed at the Ningbo-Zhoushan Port in China

Basic Sailing Terminology: Sailboat Parts Explained
Sailing is a timeless activity that has captivated the hearts of adventurous souls for centuries. But, let’s face it, for beginners, sailing can be as intimidating as trying to navigate through a dark, labyrinthine maze with a blindfold on. The vast array of sailing terminology, sailboat parts and jargon can seem like a foreign language that only the most experienced seafarers can comprehend.
Fear not, intrepid sailor, for this comprehensive guide on basic sailing terminology for beginners will help you navigate the choppy waters of sailing jargon with ease. From learning the difference between the bow and stern to mastering the intricacies of sail trim, this article will equip you with all the knowledge you need to confidently take to the seas. So hoist the mainsail, batten down the hatches, and let’s set sail on this exciting journey of discovery!
Parts of a Sailboat
Before you can begin your sailing adventure, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the different parts of a sailboat. From the sleek bow to the sturdy keel, each component plays a vital role in keeping your vessel afloat and propelling you forward through the waves.

- Hull The main body of the boat that sits in the water and provides buoyancy and stability.
- Bow The front of the boat that meets the water and helps to determine its direction.
- Stern The rear of the boat where the rudder and motor are located.
- Deck The flat surface of the boat that you stand on, which can include various features such as seating, storage compartments, and hatches.
- Cockpit The recessed area of the deck where the skipper and crew sit or stand while sailing, which allows for easy access to the sail controls and provides protection from the wind and waves.
- Keel The long, fin-shaped structure beneath the waterline that helps to keep the boat stable and upright.
- Rudder The flat, vertical surface located at the stern of the boat that is used to steer and control the direction of the boat.
- Tiller or wheel The mechanism used to steer the boat, either in the form of a tiller (a handle attached to the rudder) or a wheel (similar to the steering wheel of a car).
- Mast The tall, vertical pole that supports the sails and allows you to catch the wind and move through the water.
- Boom The horizontal pole extending off the bottom of the mast that holds the bottom edge of the mainsail.
- Mainsail The large, triangular-shaped sail attached to the mast and boom that captures the wind’s power to propel the boat forward.
- Jib The smaller, triangular-shaped sail attached to the bow that helps to steer the boat and balance the force of the mainsail.
- Rigging The network of ropes and cables that hold the mast and sails in place and help control their movement.
Sail Terminology
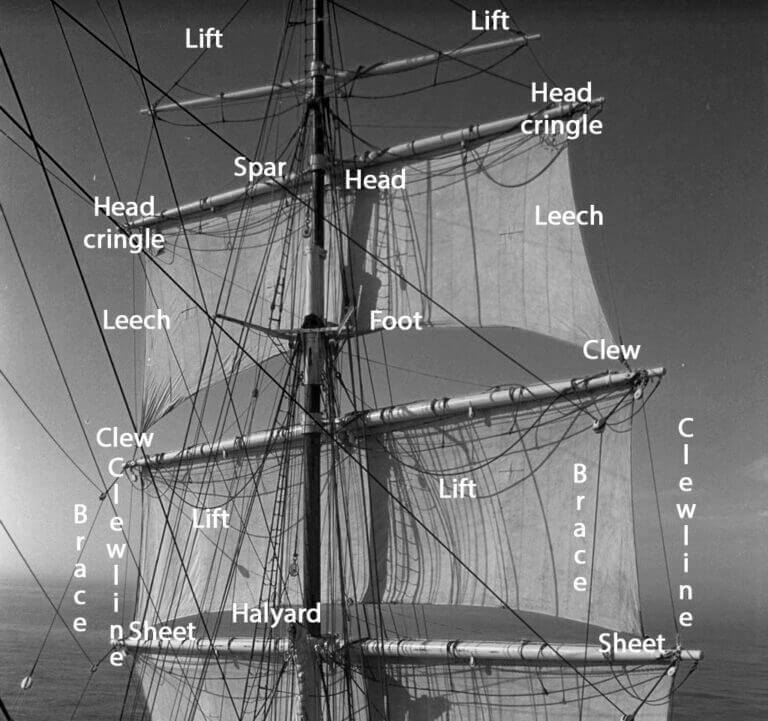
Understanding the terminology associated with sails is critical to becoming a successful sailor. Here are 12 of the most important sail terms you should know, along with brief explanations for each:

- Luff The forward edge of a sail that is attached to the mast, allowing you to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to catch more wind.
- Leech The aft edge of a sail that is attached to the boom, which helps to control the sail’s shape and release the wind as needed.
- Foot The lower edge of a sail that is attached to the boom, which helps to control the sail’s shape and power.
- Head The top of a sail that is attached to the mast and controls the sail’s overall shape and angle.
- Battens The long, thin strips inserted into the pockets of a sail to help maintain its shape and stiffness.
- Clew The bottom corner of a sail that is attached to the boom or sheet, which helps to control the sail’s shape and power.
- Tack The bottom forward corner of a sail that is attached to the boat or a line, which helps to control the sail’s shape and power.
- Sail Area The total area of a sail, which is measured in square feet or meters.
- Sail Draft The curve or depth of a sail, which affects its performance and power.
- Sail Shape The overall form and contour of a sail, which is critical for catching the wind effectively.
- Reefing The process of reducing the sail area by partially lowering or folding the sail, which can be necessary in strong winds or heavy seas.
- Furling The process of rolling or folding a sail to reduce its size or stow it away, which is often used when entering or leaving port or in rough conditions.
Wind Direction and Sail Positioning
Understanding wind direction and sail positioning is crucial for successful sailing. Here are the key terms you need to know:
Types of Wind

- Apparent Wind The wind that is felt on the boat, which is a combination of the true wind and the wind generated by the boat’s movement.
- True Wind The actual direction and strength of the wind.
Points of Sail
You can find a detailed explanation of the points of sail here

- Close-Hauled Sailing as close to the wind as possible, with the sail set at a sharp angle to the boat.
- Beam Reach Sailing perpendicular to the wind, with the sail set at a right angle to the boat.
- Broad Reach Sailing with the wind at a diagonal angle behind the boat, with the sail angled away from the boat.
- Running Sailing directly downwind, with the sail on one side of the boat.
Other Terms
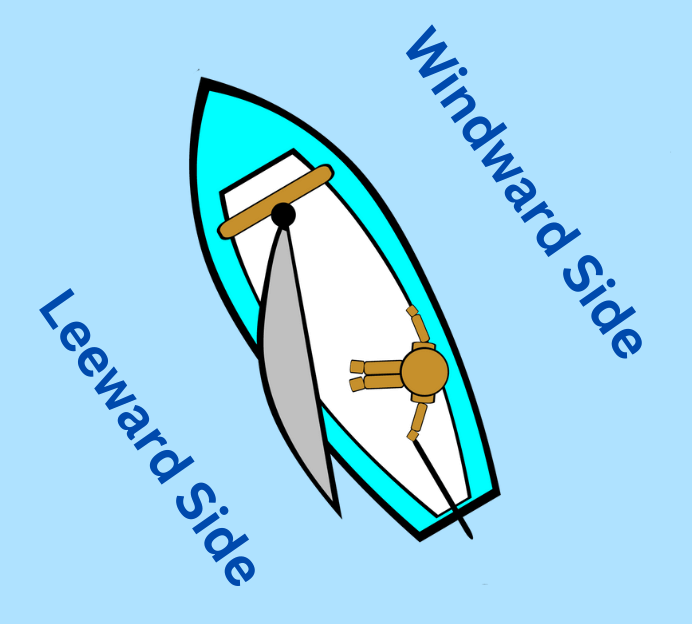
- Windward The side of the boat that is facing the wind.
- Leeward The side of the boat that is sheltered from the wind.
- Sail Trim Adjusting the sail and rigging to maximize the power and efficiency of the sailboat.
Navigation Terminology
Navigating a sailboat requires an understanding of a variety of nautical terms. Here are some of the most important terms you should know:
- Starboard Side The right side of a boat
- Port Side The left side of a boat
- Compass A device used for determining the boat’s heading or direction.
- Bearing The direction from the boat to a specific point on land or water.
- Chart A map or nautical publication that displays water depths, navigational aids, and other important information for safe navigation.
- Latitude The angular distance between the equator and a point on the earth’s surface, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Longitude The angular distance between the prime meridian and a point on the earth’s surface, measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Course The direction in which the boat is traveling.
- Plotting The process of marking a course on a chart or map.
- Waypoint A specific point on a navigational chart or map that serves as a reference point for plotting a course.

- Tacking This maneuver involves turning the bow of the boat through the wind in order to change direction. To tack , the sailor will turn the helm towards the wind until the sails begin to luff, then quickly steer the boat in the opposite direction while adjusting the sails to catch the wind on the new tack.
- Jibing This maneuver is similar to tacking, but involves turning the stern of the boat through the wind. To jibe, the sailor will steer the boat downwind until the sails begin to luff, then quickly turn the stern of the boat in the opposite direction while adjusting the sails to catch the wind on the new tack.
- Heading up This maneuver involves turning the boat closer to the wind in order to sail upwind. To head up, the sailor will turn the helm towards the wind while simultaneously trimming the sails in to maintain speed and prevent the boat from stalling.
- Falling off This maneuver involves turning the boat away from the wind in order to sail downwind. To fall off, the sailor will steer the helm away from the wind while simultaneously easing the sails out to catch more wind and accelerate the boat.
- Docking This maneuver involves bringing the boat alongside a dock or other fixed object in order to moor or disembark. To dock, the sailor will typically approach the dock at a slow speed while using lines and fenders to control the boat’s position and prevent damage.
Knots and Lines
Learning the right knots and lines to use is essential for any sailor. Here are some of the most important knots and lines to know:
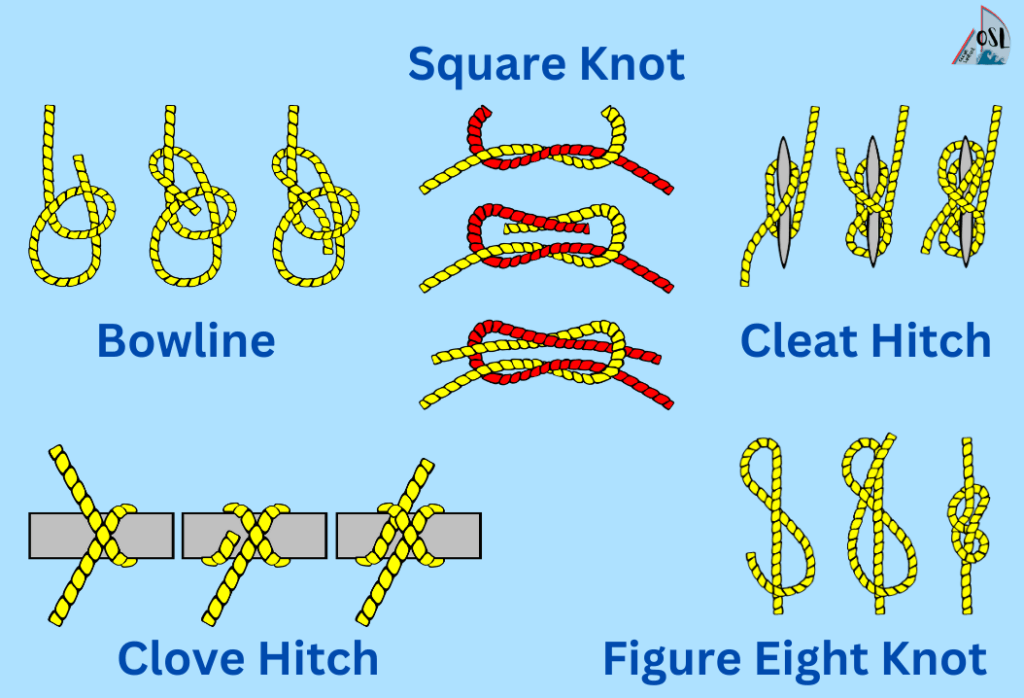
- Bowline This is a versatile knot used for many purposes, including attaching a line to a fixed object, such as a mooring or cleat.
- Square Knot A simple knot used to join two lines of the same diameter.
- Clove Hitch A quick and easy knot for attaching a line to a post or piling.
- Figure-Eight Knot A knot used to stop the end of a line from unraveling.
- Cleat Hitch A knot used to secure a line to a cleat.
- Sheet Bend A knot used to join two lines of different diameters.

- Main Halyard A line used to raise the mainsail.
- Jib Sheet A line used to control the angle of the jib.
- Mainsheet A line used to control the angle of the mainsail.
- Jib Furling Line A line used to furl the jib.
Sailing Safety
- Personal Flotation Devices (PFDs) These are the life jackets or vests that you must wear when on board to ensure your safety. Choose a PFD that fits you properly and is appropriate for your body weight.
- Tethers and Harnesses These are designed to keep you attached to the boat and prevent you from falling overboard. Make sure to clip yourself onto the boat when you’re on deck or going up to the mast.
- Man Overboard ( MOB ) Drill This is a critical safety procedure to practice with your crew. Learn how to quickly identify and recover someone who has fallen overboard.
- Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon (EPIRB) An EPIRB sends a distress signal and your location to rescue services in an emergency. Make sure it’s properly registered and in good working condition.
- Navigational Lights Ensure your boat has the required navigational lights and know how to use them properly. These lights help other boats see you in low-light conditions.
Remember that safety is always the top priority when sailing, and it’s essential to take it seriously.

Sailing Terminology Conclusion
As we come to the end of our sailing terminology crash course, it’s important to remember that the world of sailing is vast and varied. Learning even the basics can be a daunting task, but with practice and perseverance, you’ll be able to hoist your sails and set a course for adventure.
Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or just starting out, understanding the terminology is crucial to ensure a safe and enjoyable voyage. From the parts of the boat to the knots and lines, each aspect plays a significant role in the overall sailing experience.
So, as you prepare to embark on your next sailing adventure, keep in mind the importance of safety, navigation, and proper etiquette on the water. And remember, when all else fails, just hoist the Jolly Roger and hope for the best! (Just kidding, don’t actually do that.) Happy sailing!

What is the difference between apparent wind and true wind?
Apparent wind is the wind felt by the sailor on the boat, while true wind is the wind direction and speed relative to the ground.
What are the points of sail?
The points of sail are the directions that a sailboat can travel in relation to the wind. They include upwind, close-hauled, beam reach, broad reach, and downwind.
What does it mean to be “on a reach”?
Being “on a reach” means sailing with the wind coming from the side of the boat, at a perpendicular angle to the boat’s direction.
What is tacking?
Tacking is the maneuver used to turn the boat’s bow through the wind, allowing the boat to change direction while still sailing upwind.
What is jibing?
Jibing is the maneuver used to turn the boat’s stern through the wind, allowing the boat to change direction while sailing downwind.
What is the difference between windward and leeward?
Windward is the side of the boat that is facing into the wind, while leeward is the side of the boat that is sheltered from the wind.
What is a boom vang?
A boom vang is a line used to control the position of the boom, which helps control the shape and position of the sail.
What is a cleat?
A cleat is a device used to secure a line to the boat, allowing the sailor to adjust the tension of the line without having to hold onto it constantly.
What is a winch?
A winch is a mechanical device used to control lines and adjust sails. It typically consists of a drum and handle that can be turned to wind or unwind a line.
Similar Posts

Whats the Difference between Standing Rigging and Running Rigging?
Running rigging refers to the movable lines and ropes used to control the position and shape of the sails on a sailboat. Standing rigging, on the other hand, refers to the fixed wires and cables that support the mast and keep it upright. As the sun rises on another day, we find ourselves immersed in…

How Does a Marine Toilet Work?
Have you ever wondered how a marine toilet works? If you’re planning to embark on a boating adventure or just curious about the mechanism of a marine toilet, this article is for you. Marine toilets work similarly to the ones on land with a bowl, a seat, and a flushing mechanism that uses water. However,…

Mainsail Furling Systems – Which one is right for you?
With the variety of options of mainsail furling systems available, including slab, in-boom, and in-mast systems, it can be challenging to determine which one best suits your needs. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the pros and cons of each system, enabling you to make an informed decision that aligns with your sailing requirements….

What is a Sloop? Definition, Types and History
A sloop is a type of sailboat that has a single mast and a fore-and-aft rig. Sloops are a type of sailboat that has been around for centuries. They are known for their versatility and ease of handling, making them popular among sailors of all skill levels. Sloops have a single mast and a fore-and-aft…
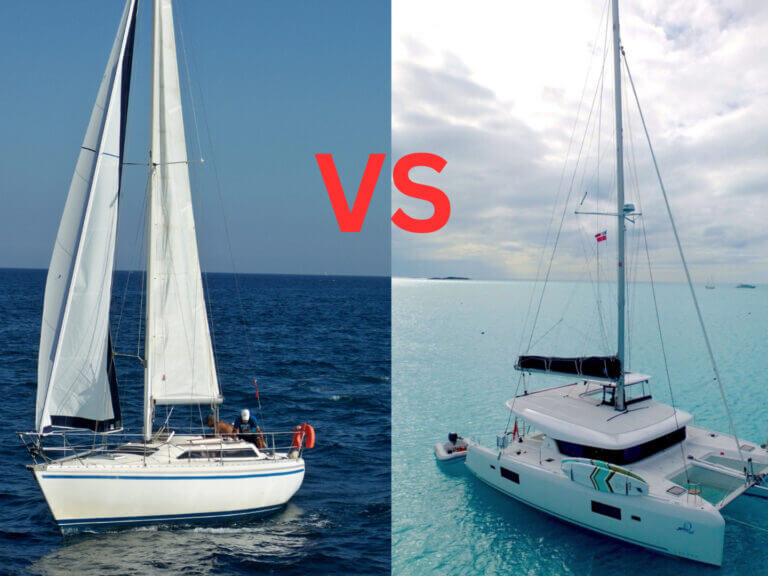

Monohulls vs. Catamarans: Which One is Best for You?
If you’re considering purchasing a sailboat, you might be wondering which type of vessel is best suited for your seafaring adventures. Fear not, for we’re here to help you weigh the differences between monohulls vs. catamarans to make an informed decision. Now, before we dive into the nitty-gritty details of hull design, sail handling, and…

Anchoring Tips for Beginners
Are you ready to set sail on a journey to become anchoring aficionados? Anchoring a sailing yacht may seem like a simple task, but let me tell you, it’s no small feat. It requires a blend of nautical knowledge, careful planning, and a dash of luck (and a pinch of salt, if you ask any…

Sailing Terminology List: 300+ Sailing Terms

There’s a massive amount of sailing terms that any sailor will eventually learn with time and it can seem daunting essentially learning a new language.
Need to know sailing terminology will help you out when communicating with your crew members and captains of other vessels, so having a sailing terminology list handy can do a lot of good.
That’s why I put together this list of common sailing terms that’ll help you out the next time you head out on the water.
Aback – A foresail when against the wind, used when tacking to help the vessel turn. Abaft – Toward the stern, relative to some object. Abeam – On the beam, a relative bearing at right angles to the ship’s keel. Aboard – On or in a vessel. Adrift – A boat drifting without being propelled. Aft – At or towards the stern or behind the boat. Aground – A boat whose keel is touching the bottom. Amidships – The middle section of a vessel with reference to the athwartships plane, as distinguished from port or starboard. Apparent wind – The wind felt aboard a moving boat. Astern – Behind the stern of the boat. Athwartships – Across the boat from side to side.
Backstay – The standing rigging running from the stern to the top of the mast, keeping the mast from falling forward. Bail – To empty the boat of water. Ballast – Weight in the keel of a boat that provides stability. Barometer – An instrument that measures air pressure, an aid to forecasting the weather. Batten – A thin wood or fiberglass slat that slides into a pocket in the leech of a sail, helping to maintain an aerodynamic shape. Beam – The width of a boat at its widest point. Beam reach – Sailing in a direction at approximately 90 degrees to the wind. Bear away – To “fall off” or head away from the wind. Bearing – The direction from one object to another expressed in compass degrees. Beating – A course sailed upwind. Below – The area of a boat beneath the deck. Bend – To attach a sail to a spar or a headstay or to attach a line to a sail. Bight – A loop in a line. Bilge – The lowest part of a boat’s interior where water on board will collect. Bitter end – The end of a line. Blanket – To use the sail or object to block the wind from filling a sail. Block – A pulley on a boat. Boat hook – A pole with a hook on the end used for grabbing hold of a mooring or retrieving something that has fallen overboard. Boltrope – The rope that is sewn into the foot and luff of some mainsails and the luff of some jibs by which the sails are attached to the boat. Boom – The spar extending directly aft from the mast to which the foot of the mainsail is attached. Boom vang – A block and tackle system, which pulls the boom down to assist sail control. Bottom – The underside of a boat. Bow – The forward part of the boat. Bowline – A line running from the bow of the boat to the dock or mooring. Bow spring – A line running from the bow of the boat parallel to the dock or mooring that stops the boat from moving forward along the dock. Bowline – A knot designed to make a loop that will not slip and can be easily untied. Breast line – A short line leading directly from the boat to the dock. Broach – An uncontrolled rounding up into the wind, usually from a downwind point of sail. Broad reach – Sailing in a direction with the wind at the rear corner (the quarter) of the boat. Approximately 135 degrees from the bow of the boat. Bulkhead – A wall that runs athwartships on a boat, usually providing structural support to the hull. Buoy – A floating navigation marker. Buoyancy – The ability of an object to float. Bulwark – A solid side wall, often about waist high, from the outside edge of the deck to prevent someone from falling overboard. Burdened vessel – The vessel required to give way for another boat when the two may be on a collision course. By the Lee – A sailboat running with the wind coming over the same side of the boat as the boom.
Cabin – The interior of the boat. Can – In the U.S., it’s an odd-numbered green buoy marking the left side of the channel when returning to harbor. Capsize – To tip or turn a boat over. Cast off – To release a line when leaving a dock or mooring. Catamaran – A twin-hulled vessel with a deck or trampoline between the hulls. Catboat – A boat with only a mainsail and an unstayed mast located at the bow. Centerboard – A pivoting board that can be lowered and used like a keel to keep a boat from slipping to leeward. Centerline – The midline of the boat running from bow to stern. Chafe – Wear on a line caused by rubbing. Chainplates – Strong metal plates which connect the shrouds to the boat. Channel – A (usually narrow) lane, marked by buoys, in which the water is deep enough to allow a vessel safe passage. Chart – A nautical map. Charter – To rent a boat. Chock – A guide mounted on the deck through which dock lines and anchor rode are run. Chop – Rough, short, steep waves. Cleat – A nautical fitting that is used to secure a line. Clew – The lower aft corner of a sail. The clew of the mainsail is held taut by the outhaul. The jib sheets are attached to the clew of the jib. Close hauled – The point of sail that is closest to the wind when the sails are hauled close to the centerline of the boat. Close reach – Sailing in a direction with the wind forward of the beam (about 70o from the bow). Coaming – The short protective wall that surrounds the cockpit or hatch. Cockpit – The lower area of the deck in which the steering and sail controls are located. Coil – To loop a line neatly so it can be stored, or a reel of line. Come about – To alter course so as to cause the bow of the boat to pass through the eye of the wind. Companionway – The steps leading from the cockpit or deck to the cabin below. Compass – The magnetic instrument which indicates the direction in which the boat is headed. Compass rose – The circles on a chart which indicate the direction of true and magnetic north. Course – The direction in which the boat is being steered. Crew – Besides the skipper, anyone on board who helps run the boat. Cunningham – A line running through a grommet a short distance above the tack of the mainsail which is used to tension the luff of the main. Current – The horizontal movement of water caused by tides, wind, and other forces. Cutter – A single-masted boat rigged with both jib and staysail.
Daysailer – A small sailboat. Dead downwind – Sailing in a direction straight downwind. Deck – The mostly flat area on top of the boat. De-power – Reducing the power in the sails by luffing, easing the sheets, or stalling. Dinghy – A small sailboat or rowboat. Displacement – The weight of the boat; therefore the amount of water that it displaces. Dock – The quay or pontoon where a boat may be tied up. Dockline – A line used to secure a boat to the dock. Dodger – A canvas protection in front of the cockpit of some boats that are designed to keep spray off the skipper and crew. Downhaul – A line used to pull down on the movable gooseneck on some boats to tension the luff of the mainsail. Draft – The depth of a boat’s keel from the surface of the water.
Ease – To let out a line or sail. Ebb – An outgoing tide.
Fairlead – A fitting that guides sheets and other lines in a way that reduces friction and therefore chafe. Fairway – The center of a channel. Fake – Lay out a line on the deck using large loops to keep it from becoming tangled. Fall off – Alter course away from the wind. Fast – To secure something. Fathom – A measure of the depth of water. One fathom equals six feet. Fender – An inflated rubber or plastic bumper used to protect a boat by keeping it from hitting the dock. Fend off – To push off. Fetch – The distance of open water to windward between the shore and the boat. Fid – A tapered spike used to open the lay of a rope when splicing. Flood – An incoming tide. Following sea – Wave pattern hitting the stern of the boat. Foot – The bottom edge of the sail. Fore – Another word for “forward”. Forepeak – An accommodation or storage area in the bow below the deck. Foresail – A jib or genoa. Forestay – The standing rigging running from the bow to the mast top and to which the foresail is secured. Forward – Towards the bow. Fouled – Another word for “tangled”. Fractional rig – When the forestay is attached to the mast some distance below the top. Foul weather gear – Water resistant clothing. Freeboard – The height of the hull above the water’s surface. Full – Not luffing. Furl – To fold or roll up a sail.
Gaff – On some boats, a spar along the top edge of a four-sided fore and aft sail. Genoa – A large foresail whose clew extends aft of the mast. Give way vessel – The vessel required, by the regulations, to give way in a collision situation. G.M.T. – Greenwich Mean Time. The time at the prime meridian in Greenwich, London, England. Now referred to as Universal Time Coordinated U.T.C. Gooseneck – The strong fitting that connects the boom to the mast. Great Circle – A line drawn on a chart which is accurate over a long distance, a section of the Earth which intersects the center of the Earth. Grommet – A reinforcing ring set in a sail. Ground tackle – Collective term for the anchor and rode (chain and line). Gudgeon – A fitting attached to the stern into which the pintles of a rudder are inserted. Gunwale – The edge of the deck where it meets the topsides. Gybe – Another alternative spelling of “jibe”.
Halyard – A line used to raise or lower a sail. Hank – A snap hook which is used to secure the luff of a foresail to the forestay. Hard a-lee – The call given to the crew that will initiate the action of tacking. Hard over – To turn the helm or tiller as far as possible in one direction. Hatch – A large covered opening in the deck. Haul in – To tighten a line. Head – The toilet on a boat as well as the top corner of a sail. Headboard – The small reinforcing board affixed to the head of a sail. Headed – A wind shift which causes the boat to head down or causes the sails to be sheeted in. Heading – The direction of the boat expressed in degrees. Head down – Changing course away from the wind. Head off – Another word for “head down”. Head up – Changing course towards the wind. Headsail – A jib/genoa attached to the forestay. Headstay – The standing rigging running from the bow to the top of the mast. Head to wind – When the bow of the boat is dead into the wind. Headway – Forward progress. Heave – To throw. Heave to – To hold one’s position in the water by using the force of the sails and the rudder to counteract each other. Holding ground – The seabed or bottom ground in an anchorage. Hove to – A boat that has completed the process of heaving to with its aback, its main trimmed, and its rudder positioned to hold the vessel close to the wind. Heavy weather – Strong winds and large waves. Heel – The lean of the boat caused by the wind. Helm – The tiller. Helmsman – The person responsible for steering the boat. Hull – The body of the boat, excluding the rig and sails. Hull speed – The theoretical maximum speed of a sailboat determined by the length of its waterline.
Inboard – Inside of the rail of the boat. In irons – A boat that is head to wind and unable to move or maneuver.
Jackstay – A wire or webbing strap attached at the front and back of a vessel along the deck to which a safety harness line may be clipped. Jib – The small forward sail of a boat that is attached to the forestay. Jibe – To change the direction of the boat by steering the stern through the wind. Jibe oh – The command given to the crew when starting a jibe. Jiffy reef – A quick reefing system allowing a section of the mainsail to be pulled down and tied to the boom. Jury rig – An improvised temporary repair.
Kedge – A smaller anchor than the main or bower anchor. Often used for maneuvering or kedging off. Kedge off – To use an anchor to pull a boat into deeper water after it has run aground. Keel – The heavy vertical fin beneath a boat that helps keep it upright and prevents it from slipping sideways in the water. Ketch – A two-masted sailboat on which the mizzen (after) mast is lower than the mainmast and is located forward of the rudderpost. Knockdown – A boat heeled so far that one of its spreaders touches the water. Knot – One nautical mail per hour.
Land breeze – A wind that blows over the land and out to sea. Lash – To tie down. Lay – To sail a course that will clear an obstacle without tacking. Lazarette – A storage compartment built into the cockpit or deck. Lazy sheet – The windward side jib sheet that is not under strain. Lead – To pass a line through a fitting or block. Lee helm – The boats tendency to turn away from the wind. Lee shore – Land which on the leeward side of the boat. Leech – The after edge of a sail. Leeward – The direction away from the wind that is the direction that the wind is blowing to. Leeward side – The side of the boat or sail that is away from the wind. Leeway – The sideways slippage of the boat in a downwind direction. Lifeline – Rope or wire supported by stanchions. Lift – The force that results from air passing by a sail or water past a keel that moves the boat forward and sideways. Line – A rope. L.O.A. – The maximum Length Overall fore and aft along the hull. Lubber line – A line on a magnetic compass to help the helmsman steer the correct course. Luff – The leading edge of a sail as well as the fluttering of a sail caused by aiming too close to the wind. Lull – A decrease in wind speed for a short duration. L.W.L. – The length fore and aft along the hull measured at the waterline.
Magnetic – In reference to the magnetic north rather than true north. Mainmast – The taller of two masts on a boat. Mainsail – The sail hoisted on the mast of a sloop or cutter or the sail hoisted on the mainmast of a ketch or yawl. Mainsheet – The controlling line for the mainsail. Marlinspike – A pointed tool used to loosen knots. Mast – The vertical spar in the middle of a boat from which the mainsail is set. Masthead – The top of the mast. Maststep – The fitting in which the foot of the mast sits. Mizzen – The small aftermost sail on a ketch or yawl hoisted on the mizzenmast. Mizzenmast – The shorter mast aft of the main mast on a ketch or yawl. Mooring – A permanently anchored ball or buoy to which a boat can be tied.
Nautical mile – Standard nautical unit of distance equal to one minute of arc of the Earth’s latitude or 6080 feet. Navigation rules – Laws established to prevent collisions on the water. No-go zone – An area into the wind in which a sailboat cannot produce power to sail. Nun – A red even numbered buoy marking the right side of a channel when returning to port.
Offshore wind – Wind blowing away from the shore and out to sea. Offshore – Away from or out of sight of land. Off the wind – Not close-hauled point of sail. On the wind – Sailing upwind in a close-hauled point of sail. Outboard – Outside the rail of a boat. Outhaul – The controlling line attached to the clew of a mainsail used to tension the foot of the sail. Overpowered – A boat that is heeling too far because it has too much sail up for the amount of wind.
Painter – The line attached to the bow of a dinghy. Pay out – To ease a line. P.F.D. – A Personal Flotation Device such as a life jacket. Pinching – Sailing too close to the wind. Pintle – Small metal extension on a rudder that slides into a gudgeon on the transom. Point – To steer close to the wind. Points of sail – Boat direction in relation to the wind. Port – The left-hand side of the boat when facing forward, a harbor, or a window in a cabin on a boat. Port tack – Sailing on any point of sail with the wind coming over the port side of the boat. Prevailing wind – Typical or consistent wind direction. Puff – An increase in wind speed. Pulpit – A guardrail at the bows of a vessel.
Quarter – The sides of the boat near the stern.
Rail – The outer edges of the deck. Rake – The angle of the mast. Range – The alignment of two objects that indicate the middle of a channel. Reach – One of the several points of sail across the wind. Ready about – The command given to the crew to prepare to tack. Ready to jibe – The command given to the crew to prepare to jibe. Reef – To reduce the area of a sail. Reeve – To pass a line through a ring or block. Rhumb line – A straight line drawn on a Mercator chart, which intersects all meridians at the same angle. Rig – The design of a boat’s masts, standing rigging and sail plan. Rigging – The wires and lines used to support and control sails. Roach – The sail area aft of a straight line running between the head and clew of a sail. Rode – The line and chain attached from the boat to the anchor. Roller-furling – A mechanical system to roll up a headsail around the headstay. Rudder – A vertical blade attached to the bottom of the hull which is used to steer the boat. Run – Point of sailing when the wind is coming from dead astern. Running rigging – The lines used to control the sails.
Sail ties – Lengths of line or webbing used to secure sails when they are dropped or to secure the unused portion of a reefed sail. Schooner – A two-masted boat whose foremast is the same height or shorter than its mainmast. Scope – The length of anchor rode paid out in relation to the maximum depth of water. Scull – To propel a boat with a single oar fixed in a notch through the transom. Scupper – A cockpit or deck drain. Sea breeze – A wind that blows from the sea onto the land. Seacock – A valve which opens and closes a hole used as an intake or discharge from the boat. Secure – The make safe or tie down. Set – The direction of the current as well as to trim the sails. Shackle – A metal fitting at the end of a line used to attach the line to a sail or another fitting. Shake out – To remove a reef. Sheave – The wheel inside a block or fitting over which the line runs freely. Sheet – A line used to control a sail by pulling it in or easing it out. Shoal – An area of shallow water. Shroud – Standing rigging at the side of the mast. Singlehanded – Sailing alone. Skeg – A vertical fin in front of the rudder. Sloop – A single-masted sailboat with mainsail and headsail. Sole – The floor in a cockpit or cabin. Spar – A pole used to attach a sail on a boat, for example, the mast, the boom, or a gaff. Spinnaker – A large downwind headsail not attached to the head stay. Splice – The joining of two lines together by interweaving their strands. Spreader – A support strut extending athwartships from the mast used to support and guide the shroud from the top of the mast to the chainplate. Spring line – A dock line running forward or aft from the boat to the dock to keep the boat from moving fore or aft. Squall – A fast moving short intense storm. Stanchions – Stainless steel or aluminum supports at the edge of the deck which holds the lifelines. Standing rigging – The permanent rigging of a boat, including the forestay, backstay, and shrouds. Starboard – The right-hand side of the boat when looking forward from the stern. Starboard tack – Sailing on any point of sail with the wind coming over the starboard side of the boat. Stay – A wire support for a mast, part of the standing rigging. Staysail – Any sail which is attached to a stay. Steerage way – The minimum speed of the boat through the water that allows the rudder to function efficiently. Stem – The foremost tip of the boat. Stern – The aft part of the boat. Stern spring – A line running from the stern of the boat parallel to the dock or mooring that stops the boat from moving backward along the dock. Stow – To store properly. Swamped – Filled with water.
Tack – To alter course so as to cause the bow of the boat to pass through the eye of the wind. Tackle – A series of blocks and line that provide a mechanical advantage. Tail – To hold the end of a line so as to keep it under tension on a winch. Telltales – Short lengths of yarn or cloth attached to the sails which indicate when the sail is properly trimmed. Tide – The rise and fall of water level due to the gravitational effects of the sun and the moon. Tiller – A long handle attached to the rudder which is used to steer the boat. Toe rail – A low rail around the outer edge of the deck. Topping lift – A line used to hold the boom up when the mainsail is lowered or stowed. Topsides – The sides of a boat between the waterline and the deck. Transom – The vertical surface of the stern. Trim – To adjust the sail controls to create optimum lift from the sails. Trimaran – A three-hulled vessel. True wind – The actual speed and direction of the wind as you would feel when standing still. Tune – To adjust the boats standing rigging. Turnbuckle – A mechanical fitting attached to the lower ends of stays allowing the standing rigging to be adjusted.
Underway – A boat that is not attached to the ground by either anchor or mooring lines. Upwind – Towards the direction of the wind. U.S.C.G. – United States Coast Guard. U.T.C. – Universal Time Coordinated. As the modern term for Greenwich Mean Time, this is the standard reference time which is used internationally for navigational information.
Vang – A block and tackle system, which pulls the boom down to assist sail control. Veer – A clockwise change in the wind direction. Vessel – Any sailboat, powerboat, or ship.
Wake – Waves caused by a boat moving through the water. Waterline – The horizontal line on the hull of a boat where the surface of the water should be. Weather helm – The tendency of the boat to head up towards the wind, this increases as the sailboat becomes overpowered. Whip – To bind together the strands at the end of a line. Whisker pole – A pole temporarily mounted between the mast and the clew of the jib. Used to hold the sail out and keep it full when sailing downwind. Winch – A deck-mounted drum with a handle offering a mechanical advantage when used to trim sheets. Windward – Towards the wind. Windward side – The side of the boat closest to the wind. Wing-and-wing – Sailing downwind with the jib set on the opposite side to the mainsail. Working sails – The mainsail and the standard jib. Working sheet – The leeward sheet that is under tension.
Yard – The horizontal spar from which a square sail is suspended. Yawl – A two-masted vessel on which the mizzenmast is mounted aft of the rudderpost.
Get the very best sailing stuff straight to your inbox
Nomadic sailing.
At Nomadic Sailing, we're all about helping the community learn all there is to know about sailing. From learning how to sail to popular and lesser-known destinations to essential sailing gear and more.
Quick Links
Business address.
1200 Fourth Street #1141 Key West, FL 33040 United States
Copyright © 2024 Nomadic Sailing. All rights reserved. Nomadic Sailing is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
Deciphering the Lingo of Sailboat Racing
March 8, 2024
We make our sport harder to understand than it should be. The combination of actual technical terms and slang can be an imposing barrier to those trying to get into sailboat racing. All too often I forget and start casually slinging around terms that make my editors go “huh?” So, we thought we would start Racer’s Edge 2024 off with a primer on frequently used terms from the race course. SpinSheet staff and readers have come up with their favorites. Here, written in totally random order (and alphabetized by my friendly editor) are the beginnings of a basic glossary.

Banging the Corner
If you immediately head all the way out to the lay line right from the start of the leg, you are “banging the corner.” Remember, once you are on the lay line, you are out of options. You can’t tack or gybe without sailing extra distance and you can no longer take advantage of any shift in the wind direction. Generally speaking, classical tactical maxims dictate staying out of the corners (away from the lay lines) until late in the leg (see lay line).
Consolidate
This refers to the age-old tactical missive “cross them when you can.” If you are looking good and are ahead of a bunch of your competition, go ahead and tack or gybe and physically cross and position yourself in front of them. “Consolidation” like this will also take you back towards the middle of the course and away from those nasty lay lines.
Ducking refers to the act of passing behind, instead of trying to go in front of a right of way (starboard tack) boat. Upwind this means bearing off to go behind. Downwind this means heading up. In either case it is important to remember that ducking is not a bad thing. It simply means you are even and want to continue going in the direction you are headed. When you tack or gybe and come back together, you will have the right of way. Usually it pays to have “last starboard.” That’s the one that will determine who gets to be ahead or behind at the mark.
Headers and Lifts
Righties and Lefties are also either a “header” or a “lift” depending on what tack we are on. A lift takes us more directly towards our upwind goal, a header farther away. Downwind this is reversed. Headers take us closer to our downward goal and lifts take us farther away. Let’s say we are back sailing upwind on port tack at our 90-degree compass heading. We get a lefty, and we are “lifted” to the point where we can sail an 80-degree heading. A righty comes through, and we can sail no higher than a 100-degree heading. We are headed. The simple rule to keep this all straight is “port higher header.” If the compass numbers that we can sail hard on the wind are getting bigger, we are headed. Smaller, and we are lifted. Of course, this is reversed on starboard tack where upwind higher numbers are good (lifts) and smaller numbers are bad (headers). And don’t forget that downwind we want headers!
Late Main Gybe
A technique for gybing a boat using an asymmetrical spinnaker where the main is held on the wrong (old leeward) side while the spinnaker is brought around to the new side first. This allows the spinnaker to fill because there is no mainsail in the way creating a wind shadow. As soon as the spinnaker fills, the mainsail is released and allowed to come over to new side. This works only in light to moderate conditions when the main boom can be held. In windier conditions you want to do a “priority main gybe,” where the mainsail comes across normally just as the boat passes dead downwind. If it is windy, you just want to get the mainsail across under control and not have it influence steering the boat.
If you are sailing windward/leeward races which go straight upwind and then straight downwind, the most common format in sailboat racing, lay lines are your boundaries. Upwind, it is the close-hauled course that allows you to make (“fetch”) the upwind mark. There is a starboard-tack and a port-tack lay line. Sailing farther to the right or left of these imaginary lines means you are sailing extra distance. Since in modern boats we also tack (gybe actually) downwind, there are also port and starboard lay lines. “Short” the lay line and you will have to sail too deep and slow to get to the mark. This is slow and painful. Go too far before gybing and you will find yourself sailing much higher than you need to or would like. Fast but extra distance. Ideally, upwind or down, the lay line allows you to sail the perfect optimal VMG course to the mark.
A move which occurs when sailing upwind when one boat tacks just ahead and to leeward of another boat sailing upwind. If executed properly and the boats are close enough, the bad air coming off the boat ahead and to leeward will force the weather boat to tack because they can no longer sail optimum VMG upwind. Of course, you must get it right. Tack too close and the weather boat feels as if they have to alter course to avoid you, making it a foul. Not far enough forward after the tack is complete and there will be no room to build speed, and the weather boat may just sail right over (“roll”) you. The rule of thumb for a proper lee bow is that you need to be able to easily cross the other upwind boat in order to pull it off. A lee bow tack is used when you want to force the other boat to go the other way. A classic tactic when on or near a lay line.
We used to simply call it wind velocity. But pressure is so much sexier. I think, as with so many of our other terms, it may have had its origins among our Kiwi brethren. More pressure means more wind, and yes, it does pressure (load up) sails. It is visible on the water. Darker streaks usually mean more pressure. It is the central focus of much onboard dialogue. “Pressure looks better on the right side of the course.” Or moment to moment as we try to squeeze the most out of the boat and help the trimmers anticipate. “More pressure in 10… 3, 2, 1; it is on us now.” Calling out increases or decreases is often a full-time job of one crew member. There are lots of associated phrases like “puff on” to indicate a big increase in wind velocity.
Righties and Lefties
We not only obsess about how much wind there is but also its constantly changing direction. Wind direction is monitored constantly via compass headings, fancy electronics that actually calculate where on the compass the wind is coming from, or from simple observation of what is happening to the headings of other boats which give clues to the changes in direction on the course in front of us. Much time is spent before a race to determine compass headings upwind on port and starboard tack. Median headings become the baseline. If we are on port sailing along at a heading of 90, but a shift in the wind makes it impossible and the best we can do is sail 100 degrees, that is a right shift or a “righty.” Conversely if we can now sail a compass heading that is less than 90 degrees, that is a left shift or a “lefty.”
There is lots of great slang when it comes to maneuvers. A “sambuca” is a gybe set where the spinnaker is hoisted as the boat is gybed around the weather mark. On boats using asymmetrical spinnakers (the vast majority these days) the sail is set up and launched on the port side. This means it has to get pulled all the way around to the starboard side of the boat during the hoist, while the boat is gybing. This takes some practice! But if you want to get immediately onto port tack, it is a trick you have to have in your bag.
Velocity made good either straight upwind or downwind. This has nothing to do with velocity made good used in navigation towards a waypoint or mark. Our VMG is all relative to getting upwind or downwind as fast as possible. It is usually measured as a percentage of our forward boat speed. Upwind if we try to sail too close to the wind (often referred to as “pinching”), we are aiming more upwind but losing speed as a result. If we sail at too wide an angle (“footing”), we will be fast but not going upwind very effectively. As always in making a sailboat go, it is striking the right balance between pinching and footing for a given condition that generates the best VMG and our best overall upwind performance. Downwind trying to sail too directly towards your objective will leave you low and slow. Too high an angle and you will be fast but not making great progress downwind. Once again, the game of optimizing VMG is about finding the balance.
We have lots of others. Clearly there is a reason why our sport is difficult to learn! Keep those cards and letters coming, and we will continue to help shed some light on the peculiar lingo of sailboat racing.
This content was orignally published on SpinSheet .
The Discussion
Good review for the start of a new season - especially for rusty geezers with failing memory cells.
This website uses cookies and collects usage statistics. Privacy Policy

Us, too. We pour that passion into each of our newsletters to help you enjoy sailing even more.
The Only 50 Sailing Terms You'll Need To Know (With Pictures)
Ever get confused by all those odd sailing terms? Starboard, tack, jib… Well, no worries. In this article, I'll go over the most important sailing terms for beginners.
This is a great resource for beginning sailors that need an overview of the most important sailing terms without drowning in it . For a comprehensive list, check out this Wikipedia glossary of nautical terms . There are A LOT of nautical terms there. But no one in his or her right mind will read through that entire page (it has 48.434 words!). There are a lot of obscure words listed that no one really uses anyways. So in this article, I've filtered out the most important ones to get you up to speed quickly. I've also added pictures so you'll know what we're talking about.
Let's jump straight in. For the sake of good manners, I have categorized them by topic. If you are looking for a specific term, just ctrl+f your way directly to it.
Here are the only 50 sailing terms you'll need to know:

Orientation
Parts of the boat, parts related to sails, other terms.
...because it isn't as easy as 'left', 'right', 'front' and 'back'. No, no.
Port is the left side of the boat. It's as simple as that. I'm not entirely sure why don't they just call it 'left' these days. The name came to existence because centuries ago, you always docked your big boat with the harbor (port) being on the left side. And the word stuck with us till today.

Starboard is the right side of the boat. If in a car, you say 'look to your right', on a boat, you say 'look to the starboard'. Again, you might as well just call it 'right'. Oh, wait… you wouldn't seem as cool if you did. Alright, let's keep calling it starboard.

The bow is the front of the boat. The word likely comes from the Middle Dutch 'boech' (nowadays spelled 'boeg'). If you call it 'front' instead, you will get your message across just as well. But it won't get you the admiring looks from those around you.

Stern is the back of the boat. That is where you, as a captain, will spend most of your time. Whether you will force your crew to call it 'stern' or let them use the word 'back', like the dry land creatures they are, is up to you. After all, you are the captain.

The windward side of the boat is the side facing into the wind. So if the wind is coming from the right side, the windward side is on the right. Unlike some of the previous ones, this term actually makes sense - at times you need to talk about a direction not fixed in relation to the boat, but rather relative to the direction of the wind.

Leeward side of the boat is the lee side. If the wind is coming from the right side, the leeward side is on the left. Note that neither windward nor leeward specify the angle of the wind. Thus even if the wind was coming 20 degrees right off of the direction of the boat, so almost from the front, left would still be considered the leeward side.

Since there are gadgets and parts on the boat that you won't see anywhere else, it only makes sense they all have their own special name. You want to know these because unlike the direction terms where you can do with 'left' and 'right', you don't want to call a tiller 'that stick thing back there'.
Helm is the boat's steering wheel. In this case, I forgive those who came up with this name, since it is shorter than 'steering wheel' and thus saves valuable time that we can spend on sailing. Though I doubt linguistic economy was the reason.

Tiller is the long stick that operates your boat's rudder. A steering stick, if you will. It has the same function as a helm does, but it is usually used on smaller boats, where a helm would take up too much space. Or by people who prefer it to a helm, since a tiller offers a bit more in terms of response.

The rudder is the long, flat piece of metal or wood that sits underwater below the back of your boat. Connected to a tiller or a helm, it is used to control the direction of your exciting voyage. By the way, since aerodynamics and hydrodynamics work in similar ways, a plane is also operated by a rudder. Though that one isn't underwater. Hopefully.

Hull is the boat's body. Whatever the shape or size, whether opened on top (like a dinghy) or closed by a deck, (like a traditional sailboat) it's all called a hull. Structures sitting on top of the deck, like a deck salon or cabins, aren't considered a part of the hull anymore.

The keel is an underwater fin below the boat's belly. The sizes and shapes vary, sometimes it is relatively short and goes deep, (fin keel) sometimes it runs from the front all the way to the back (full keel or ballast keel). It is there mainly for stability and to help maintain forward direction when sailing.

The cockpit is the area where a boat is operated from. On sailboats, it is usually in the back and it is an open area without a roof, though this varies. You will find the rudder control and winches there. In 'smaller' (below 70 ft or so) sailboats this area oftentimes doubles as a deck dining place with a table and seating.

The bimini is a sun roof or shade that is covers the cockpit, and is generally attached to a steel frame which runs over the cockpit.
This is where things tend to get confusing. There are a whole lot of parts and a whole lot of names for them. It pays off for you and your crew to know them though, as during the stormier moments, you all want to be on the same boat (ha, ha) linguistically, as every second counts.
Lines are ropes. Not much more to add here. I suppose a 'line' sounds a bit fancier than a 'rope'. One thing this article will teach you is that if there is the slightest crack in the wall of your boat, linguistic elitism will leak its way in.
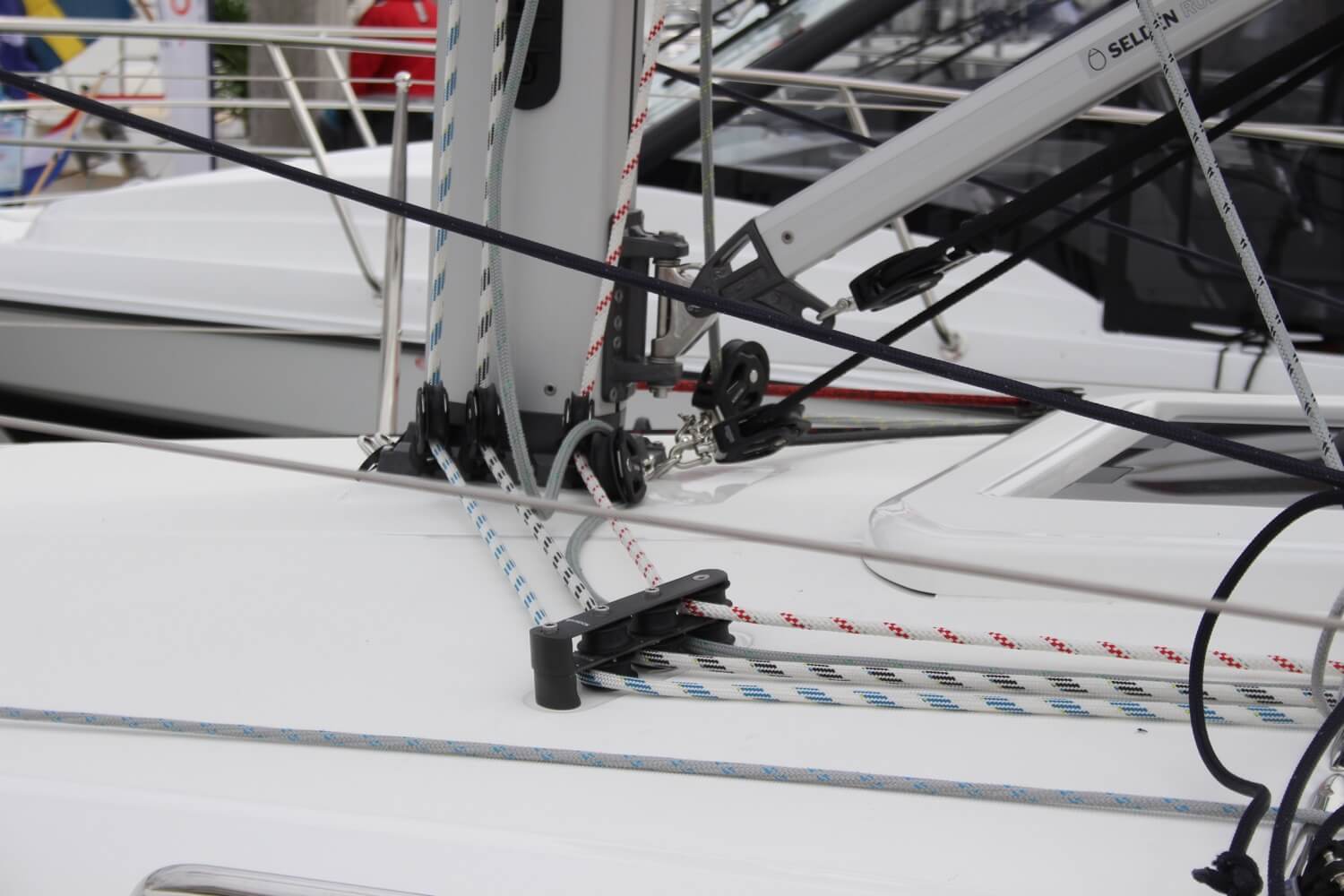

This one is quite self-explanatory. The mainsail is the main, largest sail of the boat, attached to the mast on the side and the boom at the bottom. It has a triangular shape and serves as the most important sail, the first one you should get acquainted with if you are just starting out.

The jib is the front sail of your boat, sometimes also called the genoa. That is as long as you are sailing on the traditional sloop - the classical two sail setup you see the most often. The jib is wrapped around the line that goes from the top of your mast to the boat's bow.

Spinnaker is the third type of sail you are the most likely to encounter on your travels. It goes in front of your boat and has a half balloon or kite-like shape. This is because it is constructed specifically for sailing downwind. Its purpose is to grab as much backwind as it can and drag your boat forward. It is not attached to the boat most of the time like the mainsail or the jib, instead, it is stored separately and used only when needed.

The mast is the tall, vertical pole that goes from the floor of your salon, through the deck, meters above your boat. All the sails are attached to it, also radars and lights, giving sailboats radio and visual visibility far greater than that of equally sized motorboats. Take that, ya noisy stinkies!
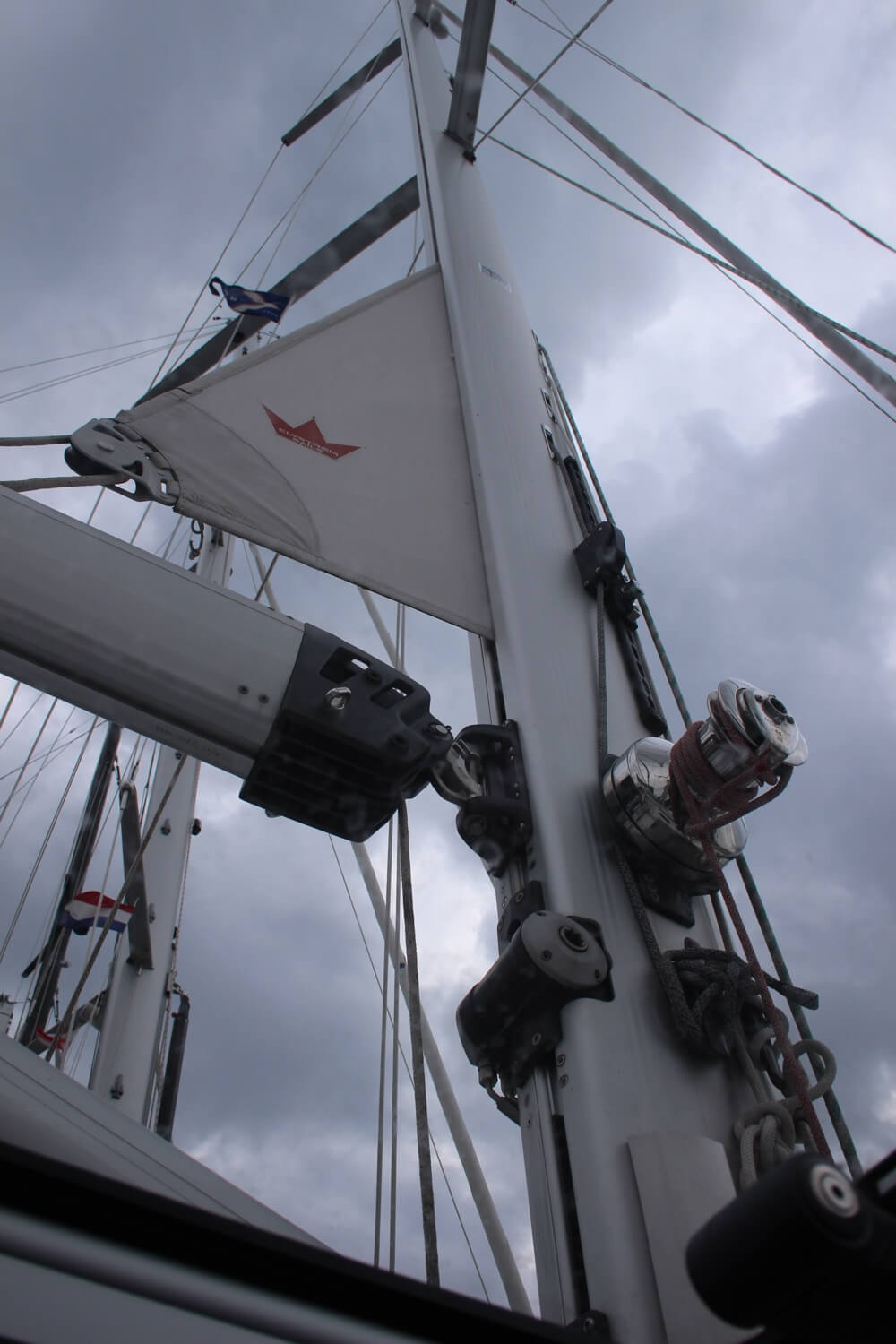

The boom is the horizontal pole right above the deck, attached to the mast at the right angle. The bottom of the mainsail is attached to it, it is used to determine its shape and direction. It is also where the mainsail is often stored, folded and covered with a protective sheet. The boom is also among the top causes of injuries on a sailboat, as in certain winds it tends to swing with force powerful enough to knock a few grown men overboard. Stay away from its reach at all times when under sail.

The forestay is the cable going from the top of the mast to the very front of the bow. It is there to hold the mast in place. Sometimes you will find people refer to it as the 'headstay'. It is often made of steel, so it is safe to hold on to it when you are pretending to be Jack on the bow of the Titanic's, the boat hits a wave and you lose your balance.
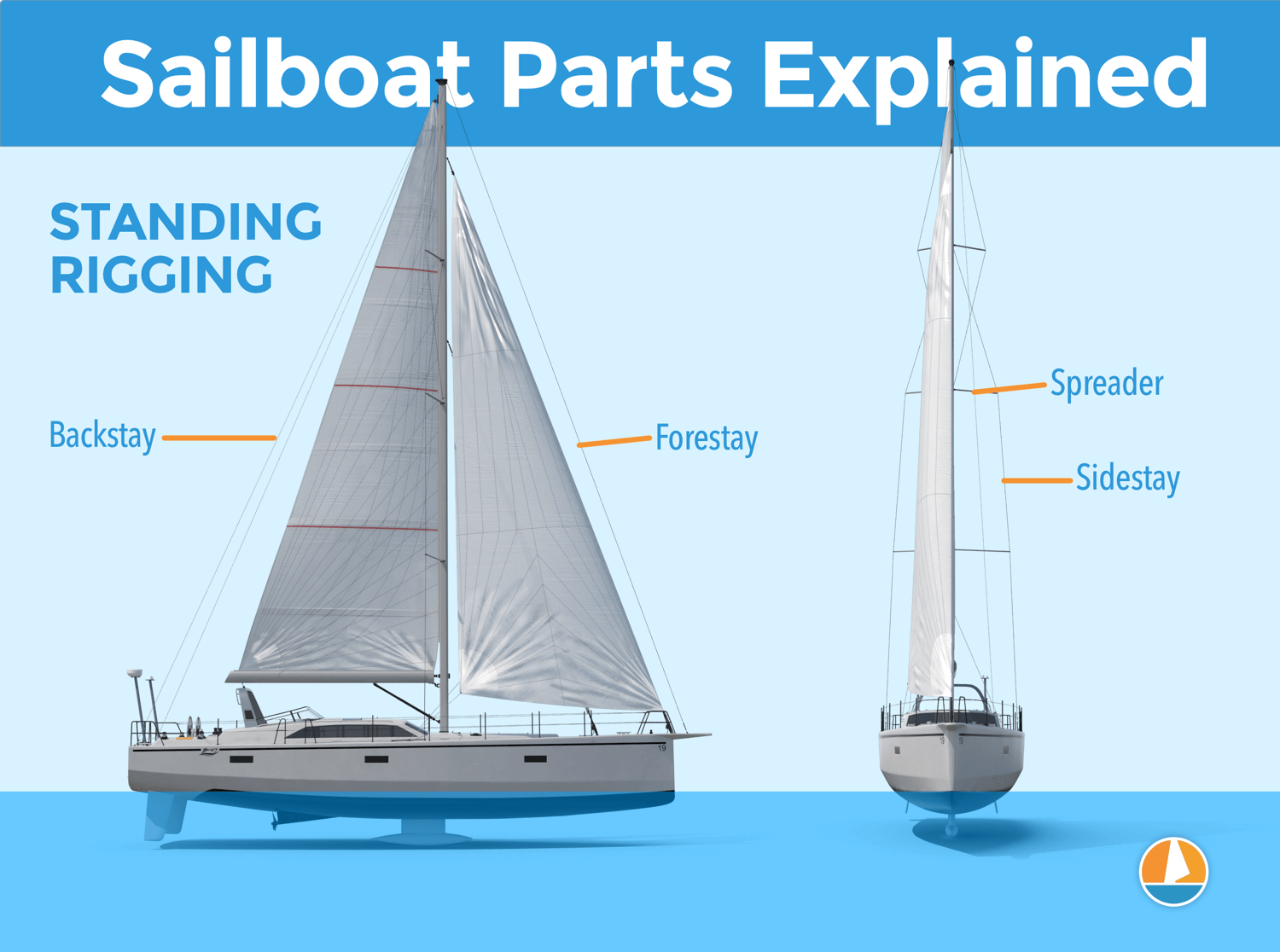
This diagram is from our guide on sailboat parts , which I really recommend for beginners. It walks you through all the most important sailboat parts in normal words.
The backstay is the cable going from the top of the mast to the very back of the boat. In many cases it is doubled at the bottom, each end attached to one corner of the back of the boat so that they don't interfere with space and provide more stability for the mast. Just as with forestay, these are made of steel.
Shrouds are the cables going from the top of the mast to the left and right side of the boat. Sometimes there are four, two on each side. Together with forestay and backstay, they make sure your mast withstands all the forces exerted on it when the wind pushes the sails.
The foot of a sail is its bottom edge. If you imagine a sail as a triangle, the base is called the foot. You probably won't use this term while sailing, but when researching proper sail trim, it is likely you will stumble upon it.
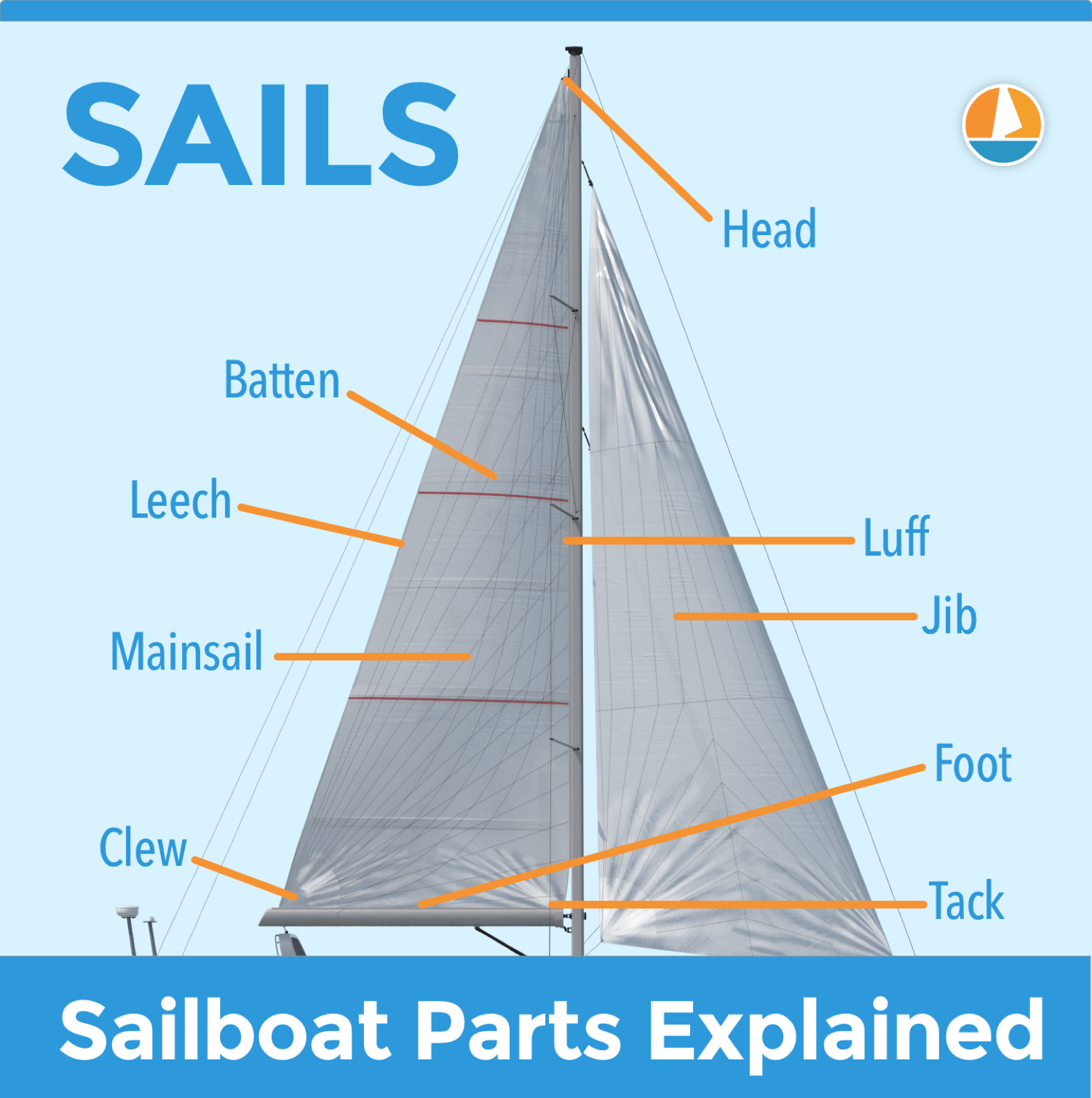
This diagram is again from our guide on sailboat parts , which I really recommend for beginners. If you're looking for a good starting point to learn your sailboat ins and outs, this article is perfect for you.
Leech of a sail is its back side edge. Thus it is the part closest to you when you are standing at the helm. Just as with the foot, this is a term quite often used when describing sail trimming techniques, since the shape of the leech determines the shape of the whole sail.
Luff of a sail is its front side edge. Thus the part the furthest from you when you are standing at the helm. For mainsail, it is the edge that is right next to the mast, for the foresail it is the edge right next to the forestay. Just as with foot and leech, the shape of these edges determines the overall shape of the sail so you will most likely encounter these terms in trimming lessons and tutorials.
The head of a sail is its top corner. On a traditional sloop, you will have the 'main head' and the 'jib head'. There is usually a reinforcing patch of some kind on these corners, as you will find a hole in them to which a line is attached.
It's also something else entirely, but more on that later ...
Halyard is the line attached to the sail head. On your boat, you will most likely have two. The 'main halyard' which is what you use to hoist your mainsail if it is folded on the boom, and the 'jib halyard' which holds the jib head up.
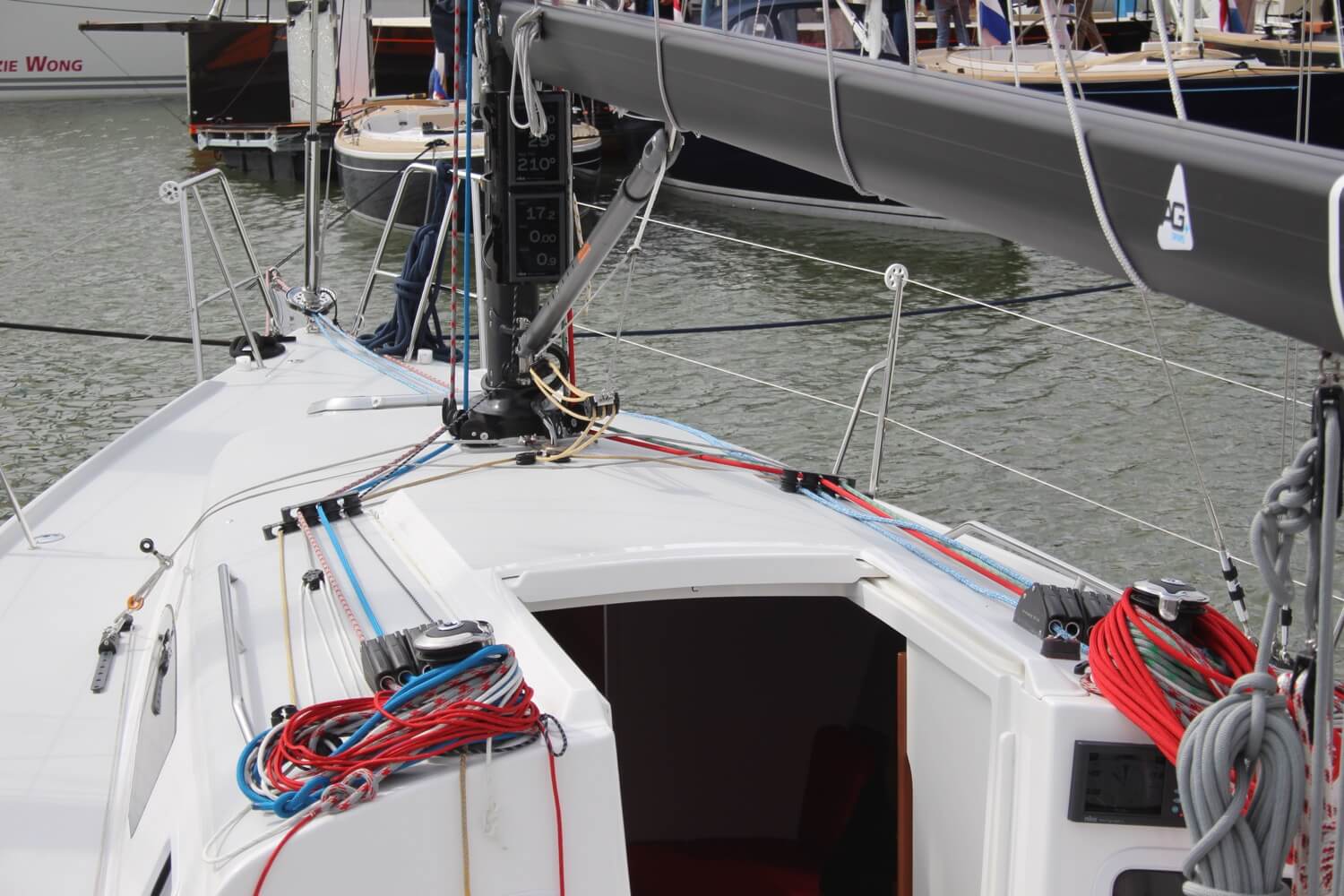

Clew of a sail is its back corner. The line attached to the 'main clew' will be used to hoist your mainsail if it is wrapped inside of the mast. The line attached to the 'jib clew' will be used to open the jib on most sailboats since jibs are most often wrapped around the luff.
Telltales are light, usually cotton or wool pieces of ropes attached to a sail, showing you the airflow around it. These are important because they help you determine if your trim is effective or not. Because of the material they are made of, you might sometimes encounter them being called 'woolies'.
Vang, or a 'boom vang' is a device pulling the boom down. This is important because it controls the tension of the mainsail, influencing its shape greatly. You won't find it on every boat though. Holiday cruisers often don't have it, as it is a piece of equipment focused on performance and thus not necessary for your average trip.
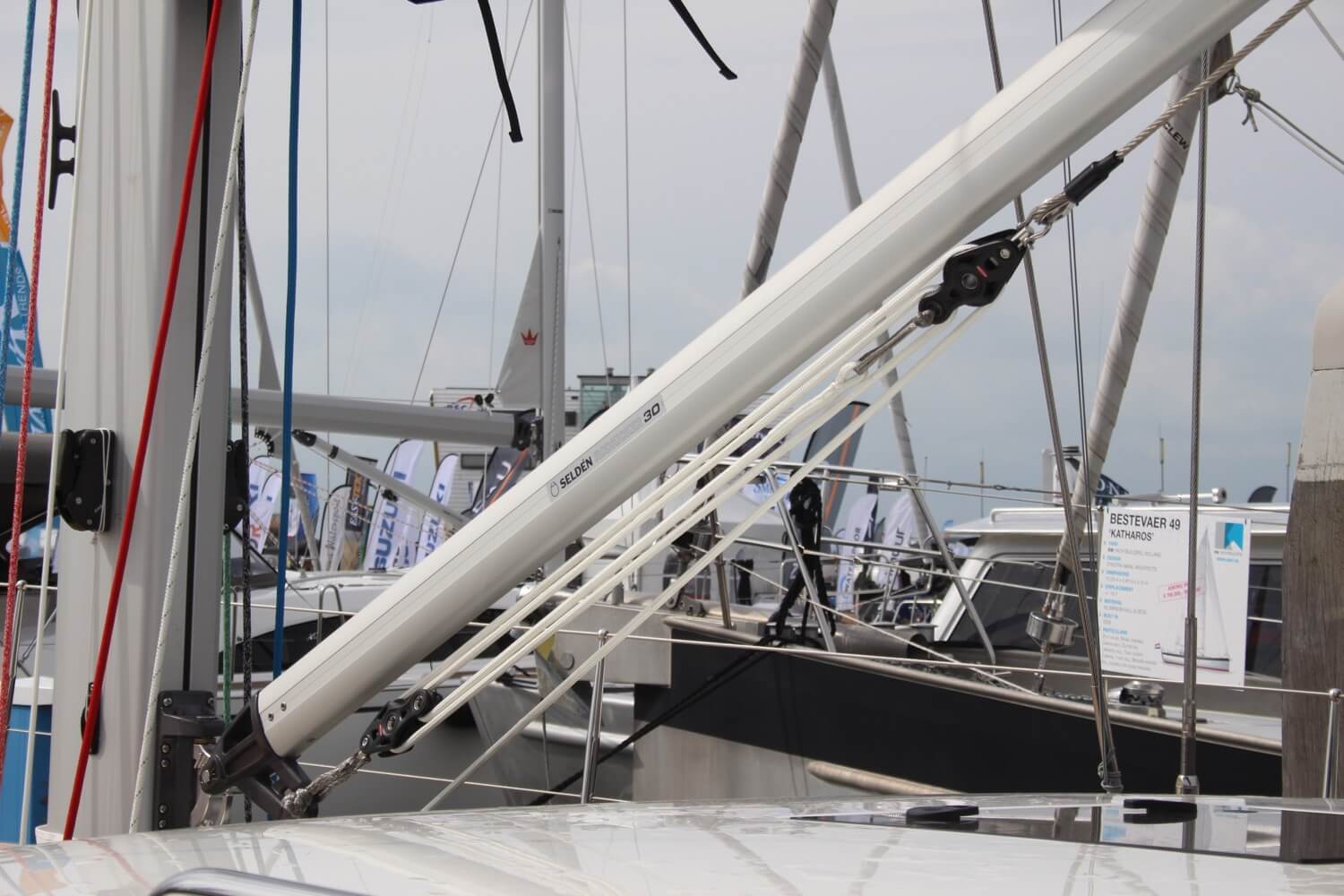

Topping Lift
The topping lift is a line that is attached to the aft (back) end of the boom and runs to the top of the mast. It supports the boom whenever you take down the mainsail.
Also referred to as a 'horse', the traveler is a side to side track to which the boom is attached, allowing the control of the extent to which the boom goes off the centerline. This is important especially if the wind is blowing from behind and you need to control the angle of the mainsheet.

Outhaul is the line attached to the mainsail or the jib clew, allowing the control of the foot tension. This is important for determining the sail shape - for instance in stronger winds, you want the foot to be more tense to achieve a more effective airflow as opposed to slower winds where you can allow the foot to arch more.

Reefing is reducing the sail area to lessen the power exerted on it by the wind. You may want to reef if the wind is getting too strong for your boat, or if it is changing too rapidly, as an overpowered boat is difficult to control. Fun fact: they say that when you feel you need to reef because the wind got too strong, it is already too late to reef.

A batten is a slat placed horizontally in the body of the sail to support its shape. You will not find them on all sailboats, it is a performance-enhancing element that many cruisers lack. It helps tremendously as without it, sails tend to belly out and lose their shape under certain conditions.
The cleat is a piece of fitting where a line can be secured and immobilized, even if under great tension. It usually consists of two cogwheel-like pieces fastened close to each other, in the middle of which the rope is placed, unable to move thanks to friction. This type is great as it allows for a quick release. Sometimes though, it is a simple piece of metal or plastic where the rope is tied.
...and then there are all those things that just float around you when sailing, those little things that are the reason for you having to carry a dictionary in your pocket.
Fenders are bumpers allowing some contact with other boats or piers while docked, without scraping the paint. They are often balloon-shaped, made of rubber or some relatively soft material. They are usually attached to the boat's railing and you move them around as you need.

The beam is the width of the boat. Could be just called width, I know. The word comes from the fact that there are transverse reinforcing beams in the boat hull and deck. Next time you are choosing your charter boat for holidays, you will know what this attribute means.
True wind is the actual direction and speed of the wind. This is different than the apparent wind, which is wind direction and speed relative to the boat. Apparent wind is a combination of the true wind and the headwind, which is the wind the boat experiences solely by being in motion.
The berth is a sleeping space on a boat. Thus if a boat has eight berths, it means eight people can comfortably sleep on it. Note that this often includes the salon couches, so a berth is not necessarily a space in an actual bed for one person.
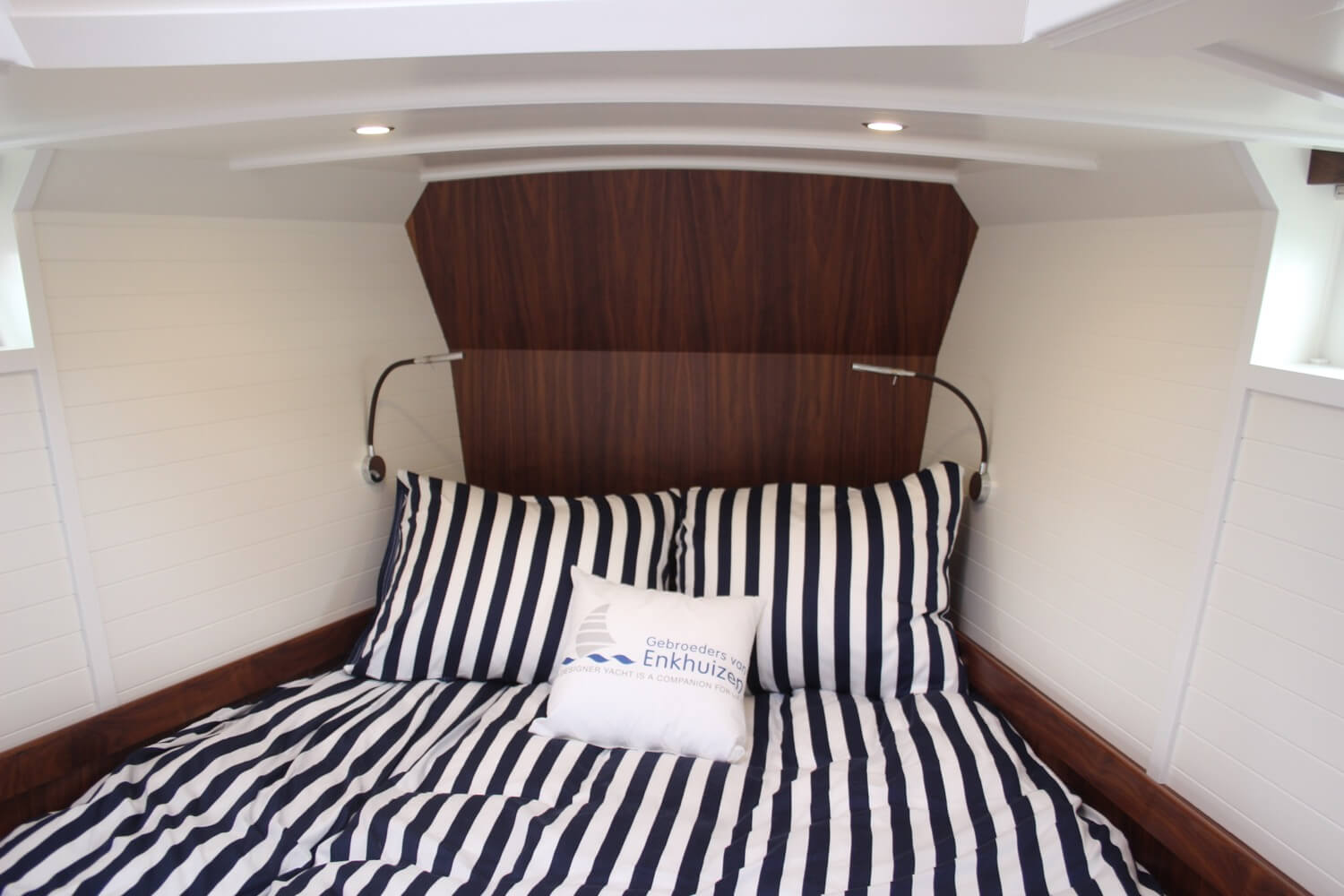

Boat's draft is the distance from the water surface to the deepest point of the boat. In other words, the draft is the minimum water depth you can go to and not scrape your hull or keel. Better double this number when sailing, just to be safe, as hitting the seabed can have disastrous consequences.
Tacking is zig-zagging towards your destination. It is necessary in case your destination is in the direction of the wind since sailboats can not go directly into it. Since the closest to the wind direction you can sail is around 45 degrees, you have to change direction left and right from your desired course.

This diagram is from our guide on sailing into the wind for beginners , which explains in 7 simple steps how to get good upwind sailing performance.
Bareboat is a boat without a skipper. You will encounter this term in boat charters and it means you rent the boat without any crew, thus you need to operate it yourself. It is the best way to sail unless you enjoy living in close proximity to a sea wolf who you also have to feed.
The chart is a nautical map. It differs from classical maps as it depicts information relevant for a sailor - water depth, navigational hazards, seabed material, anchorages and so on. Formerly made of paper, these days made of ones and zeros. As is everything in this digital world.
We have a guide that explains all the different chart types clearly for beginners - read it here .
Galley on a boat is its kitchen. Also a medieval warship, but if you find this term in a boat's description, war is not likely what they have in mind.

Heads on a boat is the bathroom. Though in all my years of sailing I have never ever heard anybody use this term instead of a 'bathroom'. I suppose saying that you are going to use the heads just sounds odd.
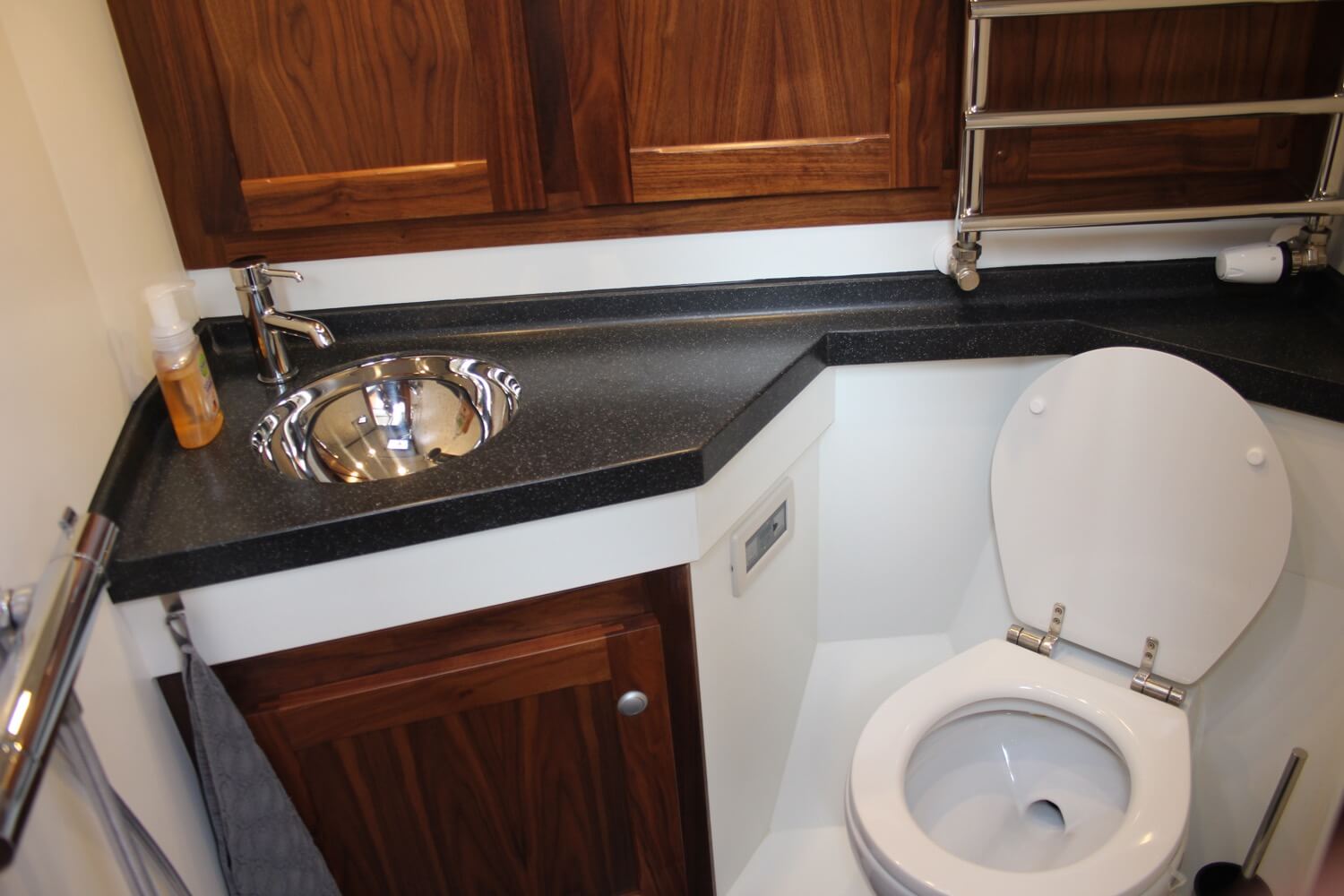

A knot is the unit of speed of boats. It is equal to one nautical mile per hour. That is 1.852 kilometers per hour or 1.5078 miles per hour. Though a bit confusing and annoying at times, you will have to get used to this, since most of your boat's instruments will use this unit. It dates all the way back to the seventeenth century when boat's speed was measured with a rope with knots tied on it.

Mooring is attaching the boat to a buoy that is anchored to the seabed. This is usually a cheaper option to docking in a marina. It also means larger space between the boats anchored in the same area, thus more privacy. Though you will have to use your dinghy to get to shore instead of just stepping on the pier directly from your deck.

A salon on a boat is its living room. On smaller boats, it is usually in the same room as the boat's kitchen and the captain's corner with navigation instruments.

A skipper is the captain of a sailboat. If you ask me, the word 'captain' is much better than a skipper, which to me sounds like a small boy who sits on the shore the whole day, skipping stones. But hey, who am I to talk.

A monohull is a classical boat with a single hull. A boat with two hulls is called a catamaran, or a 'cat'. Although rare, there are also trimarans, boats with three hulls. Multihulls with four or more hulls do happen but they are an unnecessary freak of nature.

So there you have it. Fifty sailing terms you will encounter the most when traveling or learning. I know you might think some of them are a bit unnecessary since they have a perfectly fine 'real world' equivalent. I agree. But until the tradition changes, you might want to get some of these under your skin.
A boat's freeboard is the distance from the upper deck to the waterline. Classic yachts have low freeboards, so they appear to lay deeper in the water, as opposed to more modern yachts, which have a higher freeboard. It literally means 'free-board' : the amount of visible board.
The lunch hook is a light anchor setup that is used to moor small yachts temporarily. It typically uses a lightweight anchor on a short scope that takes little effort to set. The lunch hook is only used when the crew is on board and will be monitoring the anchor.
In naval architecture and ship design: “Head” = WC = Bathroom. A toilet is still a toilet. The toilet is in the head. In olden day, the toilet was a hole in the head.
Hi Rich, you’re absolutely right. I’ve corrected the error. Thanks for pointing it out.
A nautical mile is one minute of a degree, so if you travel 60 nautical miles that means you have gone 1 degree around the “globe”. (Note: arc length not actual length.) This is the original definition. As such the average was agreed upon and the lengths given a standardization. Which you mentioned.
As such 1 knot is to travel one nautical mile in an hour.
Also 1.5078. I think you made a mistake as it should be 1.1508 miles to a nautical mile.
Thanks for the information. Sorry about being a pedantic mathematics teacher.
So, where is the “nautical mile” calculated from, the equator or one of the tropic lines?
Just to clarify a nautical mile. If you draw an imaginary line from the North Pole or South Pole to the center of the Earth and draw another line from the center of the Earth to any point on the equator, it forms a right angle, which is 90 degrees. This equates to latitude. The equator is 0 degrees and the poles are 90 degrees. Your latitude is the angle that you are north or south of the equator. Each degree of latitude is divided into 60 minutes. A minute of latitude is the same distance matter where you are on Earth. It is 6,076 feet. This is the length of a nautical mile. A statute mile is 5,280 feet, so a nautical mile is 1.1508 statute miles.
Thank you very clear and well explained. Hopefully I’ll remember The Fifty
KöhnSharkösz
Really? No gunwale? No transom? Those or basic terms to the Washington State Boater Education Card required to operate watercraft here. Definitely more of a “need to know” than bimini.
Thank you, those definitions and explanations were clear, thorough, and helpful. I’m really glad I found my way (somehow) to your webpage.
Leave a comment
You may also like, 17 sailboat types explained: how to recognize them.
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.

How Much Sailboats Cost On Average (380+ Prices Compared)

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

Sailboat Parts Explained: Illustrated Guide (with Diagrams)

How To Live On a Boat For Free: How I'd Do It
- +1-858-652-2046
Member Login
- Sailing Resources - Get Listed Today
- Destinations
- How-To Guides
- Fun & Entertainment
- Maintenance
- Personalities
- Food Recipes
- Drink Recipes
- Listings Directory
- Gear Reviews
Top 100 Essential Sailing Terms Every Crew Must Know

In the world of sailing, communication is key. The complex lingo utilized by sailors is far more than just jargon — it's an integral part of safe and effective teamwork. Here Cruisers Directory, we aim to help crew members brush up on sailing vernacular or beginners get a head start with our carefully curated list of the top 100 essential sailing terms everyone should know. Whether you are an experienced sailor or a complete novice, this comprehensive guide is your indispensable companion at sea.
1. Abeam: At a right angle to the length of the boat. 2. Aft: Towards the stern (back) of the ship. 3. Amidships: The middle section of a boat. 4. Anchorage: A designated area where vessels anchor. 5. Astern: Behind the boat. 6. Ballast: Weight added to the boat to increase stability. 7. Beam: The widest part of a boat. 8. Berth: The bed on a boat; also a slip in a marina. 9. Bilge: The lowest part of a boat's interior hull. 10. Binnacle: A casing on the deck that holds the ship’s compass. 11. Boom: The horizontal pole extending from the mast to hold the bottom of a sail. 12. Bow: The front part of the boat. 13. Bowsprit: A pole extending forward from the boat's bow, to which the forestays of a ship are fastened. 14. Broad Reach: Sailing with the wind coming from behind, and slightly to the side, of the boat. 15. Buoy: A floating device that can have many uses, as to mark a channel, anchor a boat or indicate position. 16. Capsize: When a boat turns over in the water. 17. Chart: A map used for navigation. 18. Cleat: A fitting to which lines are made fast. 19. Coaming: A raised lip around a hatch to prevent water entry. 20. Cockpit: Area towards the stern of the boat where the helm is. 21. Crew: The people who operate a ship. 22. Deckhand: A member of the crew who helps perform manual tasks on a boat. 23. Displacement: The weight of water displaced by a floating boat, giving the vessel's weight. 24. Doldrums: A nautical term referring to a calm sea with no wind. 25. Draught/Draft: The depth of water needed to float a vessel. 26. Ebb: The outgoing or falling tide. 27. Fathom: A measurement of depth in the sea (6 feet). 28. Fender: A cushioning device used to protect the boat. 29. Foresail: Any sail set forward of the main mast. 30. Freeboard: The distance from water to the lowest point of the boat's deck. 31. Galley: The kitchen on a boat. 32. Gybe/Jibe: To change direction when sailing downwind. 33. Halyard: A line (rope) for hoisting (raising) the sails. 34. Head: The bathroom on a boat. 35. Helm: The wheel or tiller controlling the rudder. 36. Hull: The main body of the boat. 37. Jib: A sail set forward of the mast. 38. Keel: The boat's backbone; a weighted structure at the bottom of the hull, giving the boat stability. 39. Knot: A measurement of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour. 40. Latitude: The distance north or south of the equator, measured in degrees. 41. Leeway: The sideways drift of the boat caused by wind or currents. 42. Longitude: The distance east or west of the prime meridian at Greenwich, England. 43. Main Sail: The primary and largest sail on a boat. 44. Mast: Vertical pole on a boat which holds the sails. 45. Mooring: An arrangement for securing a boat to a mooring buoy or a pier. 46. Nautical Mile: Distance measurement at sea, which is about 1.15 statute miles. 47. Navigation: The science of plotting a course for a boat. 48. Port: When facing forward, the left side of the boat. 49. Quartermaster: The person in charge of steering the ship. 50. Quay: A stone or concrete platform lying alongside water for loading and unloading ships. 51. Reef: To reduce the area of a sail. 52. Rudder: The steering device mounted at the stern of the ship. 53. Sail: Fabric attached to the mast that catches the wind and propels the boat. 54. Salon/Saloon: The living area in the boat, often part of the galley. 55. Seaworthy: A boat able to safely navigate through waters. 56. Skipper: The captain or master of a boat. 57. Starboard: When facing forward, the right side of the boat. 58. Stern: The back part of a boat. 59. Tack: To change the boat's direction by moving the bow through the wind. 60. Tender: A small boat used to ferry people and supplies to and from a larger boat. 61. Tide: The rise and fall of the ocean's surface. 62. Transom: The flat surface forming the stern of a boat. 63. Trim: Adjustment of the sails to optimize performance. 64. Vessel: Another name for a boat or ship. 65. Winch: A device used to pull in or let out ropes or cables. 66. Yacht: A pleasure boat, can be powered by wind, motor or both. 67. Yaw: The swaying motion of a boat moving from side to side off its course. 68. Zephyr: A light wind. 69. Hoist: To raise something, often a sail. 70. Leech: The aft (back) edge of a sail. 71. Jib Sheet: The line that controls the jib. 72. Bowline: A type of knot. 73. Clew: The lower corner of a sail. 74. Fluke: The part of the anchor that digs into the bottom. 75. Gimbal: A device that keeps an object level. 76. Hatch: An opening in the deck to the interior. 77. Heave: The vertical rise and fall of a boat. 78. Inboard: More towards the center of a vessel. 79. Kedge: A light anchor used in kedging or warping a boat. 80. Luff: The forward edge of a sail. 81. Pelorus: A navigational tool used to measure angles between objects. 82. Rhumb Line: A line on the earth's surface that cuts all meridians at the same angle. 83. Sloop: A one-masted sailing boat with a mainsail and jib rigged fore and aft. 84. Telltale: A piece of material attached to a sail to indicate wind direction. 85. Vang: A line used to control the boom's movement. 86. Waterline: Where the hull meets the surface of the water. 87. Xebec: An historic sailing ship with lateen sails used mostly in the Mediterranean Sea. 88. Yawl: A two-masted sailing vessel, similar to a ketch but with a smaller mizzen mast. 89. Zephyr: A light or west wind. 90. Figure Eight Knot: A stopper knot. 91. Genoa: A type of large jib or staysail which overlaps the main sail, sometimes eliminating it. 92. Impeller: The rotating part of a centrifugal pump. 93. Jackline: A line used to clip on a safety harness. 94. Ketch: A two-masted sailboat, the aft mast (mizzen) is shorter and set aft of the rudder post. 95. Log: A record of courses or operation. 96. Mizzenmast: The mast aft of a ship's mainmast. 97. Noon Sight: A sextant observation of the sun at noon to determine latitude. 98. Overboard: Over the side or out of the boat. 99. Pintle: The pin or bolt on which the rudder pivots. 100. Quarter: The sides of a boat between the stern and the midship.
Leave Comment Below
- Get Notified by Email for:
- Any New Comments
- Only Replies to My Comments
- Stop Following Comments
- Not a Registered User? Create Free User Account
- Are You a Local Business? List Your Company Now
Search Website
Recent reviews.

If you want the best sevice for your boat, Yanira is the best pers... View More

Overall a great restaurant. Kinda on a small scale, we heard so much ... View More
I've eaten wings in a lot of places including Buffalo. This place han... View More
This was last-minute stop for an early dinner and I’m glad we did! ... View More
- Finding sailing resources is easy by searching our trusted network of top-rated sailing resources.
- How It Works
- List Your Company
- Browse Categories
- Browse Locations
- Cruisers Directory
- All Rights Reserved
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
Join Our Newsletter
The basics of sailboat anatomy and terminology
Understanding sailboat anatomy and terminology is crucial for safe and efficient sailing, whether you're a beginner or a seasoned sailor.
The Basics of Sailboat Anatomy and Terminology
Welcome to the first installment of our Sailing Basics series! In this article, we’ll be diving into the world of sailboat anatomy and terminology. Whether you’re a complete beginner or a seasoned sailor looking for a refresher, this comprehensive guide will help you navigate the ins and outs of sailboats and their various components.
As you embark on your sailing journey, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the different parts of a sailboat and the terms used to describe them. This knowledge will not only help you communicate effectively with fellow sailors but also ensure that you can safely and efficiently operate your vessel.
So, without further ado, let’s set sail and explore the basics of sailboat anatomy and terminology!
The hull is the main body of the sailboat, providing buoyancy and stability in the water. It’s typically made of fiberglass, wood, or metal, and its shape and design can vary depending on the type of sailboat. The hull is divided into several sections, including the bow (front), stern (rear), port (left side), and starboard (right side).
The keel is a long, flat structure that extends from the bottom of the hull and runs along its centerline. It serves several purposes, including providing stability, preventing the boat from being blown sideways by the wind, and acting as a counterbalance to the force of the sails. There are different types of keels, such as fin keels, full keels, and wing keels, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Located at the stern of the boat, the rudder is a flat, vertical blade that helps steer the sailboat by controlling its direction in the water. It’s connected to the tiller or wheel, which the helmsman (person steering the boat) uses to turn the rudder and change the boat’s course.
The deck is the horizontal surface that covers the hull and provides a platform for crew members to stand on and operate the sailboat. It’s usually made of the same material as the hull and can be divided into several areas, such as the foredeck (front), cockpit (middle), and aft deck (rear).
The cockpit is the central area of the deck where the crew operates the sailboat. It typically contains the helm (tiller or wheel), engine controls, and various instruments, such as a compass, GPS, and wind indicators. The cockpit is also where the crew can access the cabin below deck.
Lifelines are a series of cables or ropes that run along the perimeter of the deck, providing a safety barrier to prevent crew members from falling overboard. They’re usually attached to stanchions (vertical posts) and may also include gates for boarding the boat from a dock or dinghy.
Mast and Rigging
The mast is a tall, vertical pole that supports the sails and rigging. It’s usually made of aluminum or carbon fiber and can be stepped (attached) to the keel or deck, depending on the sailboat’s design. The rigging consists of various lines, cables, and hardware that connect the mast, sails, and hull, allowing the crew to control the sails and maneuver the boat.
Standing Rigging
Standing rigging refers to the fixed lines and cables that support the mast and maintain its position. The main components of standing rigging include:
- Shrouds : Cables that run from the top of the mast to the sides of the hull, providing lateral support.
- Stays : Cables that run from the top of the mast to the bow (forestay) and stern (backstay), providing fore-and-aft support.
Running Rigging
Running rigging consists of the lines and hardware used to control the sails, allowing the crew to raise, lower, and adjust them as needed. Some key components of running rigging include:
- Halyards : Lines used to hoist (raise) the sails up the mast.
- Sheets : Lines used to control the angle of the sails relative to the wind.
- Outhaul : A line used to adjust the tension of the mainsail along the boom.
- Cunningham : A line used to adjust the tension of the mainsail along the luff (front edge).
Sails are the primary means of propulsion for a sailboat, harnessing the power of the wind to move the boat through the water. There are two main types of sails: mainsails and headsails.
The mainsail is the largest sail on the boat and is attached to the mast and boom. It’s typically triangular in shape, with its leading edge (luff) connected to the mast, its bottom edge (foot) connected to the boom, and its trailing edge (leech) left free. The mainsail is controlled using the mainsheet, outhaul, and cunningham.
Headsails, also known as jibs or genoas, are smaller sails located in front of the mast. They’re attached to the forestay and are used to improve the boat’s performance, especially when sailing upwind. Headsails can be controlled using sheets and may be furled (rolled up) when not in use.
Now that you have a basic understanding of sailboat anatomy and terminology, you’re well on your way to becoming a confident and knowledgeable sailor. As you continue to explore the world of sailing, you’ll undoubtedly encounter more specialized terms and components, but this guide should serve as a solid foundation for your ongoing education.
In the next installment of our Sailing Basics series, we’ll be covering essential sailing skills, such as tacking, jibing, and docking. Until then, fair winds and smooth seas!

- O’pen Skiff Purchase Page
- ILCA – Element 6
- RS Sailboats
- Sunfish – Recreational
- Sunfish – Race Version
- Sunfish Sails
- LaserPerformance Sunfish Parts Price List
- 420 – Zim Sailing
- Finding the Right Laser Rig: Formula
- Racks by Dynamic Dollies and Racks
- Load Rite Trailers
- Load Rite Sunfish Trailer
- **NEW** LoadRite for Sailboats
- Sunfish Dolly by Dynamic
- Optimist Dolly by Dynamic
- How to Apply Laser Sail Numbers
- Applying Laser Sail Numbers
- North Sails for LaserPerformance Dinghies
- About/Contact
Sailboat Racing Terms – Survey

Ten question survey S0, I picked ten words or phrases that seem pretty user friendly. Honestly, I hadn’t heard of all of them, but maybe most people who sail have.
So, a sailboat racing terms survey Let us know if these are terms you know, and if you know them do you actually use them while out on the race course.
The survey link: surveymonkey.com/s/KLZLHZ9
Results as they come in: https://www.surveymonkey.com/results/sm-p88llvfv/.
And if you can’t get enough sailboat racing terms Check out Sailorspeak: The Complete Insider’s Guide to Yacht Racing Terms, Jargon & Slang by Bob Roitblat

You can find an interview with Bob Roitblat at Dock Talk
Excerpt from Dock Talk blogspot:
“SAILORSPEAK” a new book by Bob Roitblat does a good job of summarizing some of the commonly used terms into one easy reference book. Bob has been racing in the Beneteau First 36.7 fleet aboard Steve Pelke’s “Stingray ” and has recently undertaken being an author. “SS” is his first entry into being a writer.”
Share this:
- Click to email this to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)

THE MELGES 15!
THE ROCKET! Built in the USA
SUNFISH – SAIL A CLASSIC!
Recent Posts

Hours & Info
Search products.
Contact us:
Any questions about the sailboats we sell, or the services we provide? We’re always eager to talk sailing and would enjoy helping you with any of your sailing needs. Contact Us

Designed by WPZOOM

- Find A School
- Certifications
- North U Sail Trim
- Inside Sailing with Peter Isler
- Docking Made Easy
- Study Quizzes
- Bite-sized Lessons
- Fun Quizzes
- Sailing Challenge

The Anatomy of a Boat
By: Zeke Quezada, ASA Equipment , Learn To Sail , Sailboats
Do You Know the Parts of a Boat
Learning to sail is not just about feeling the wind in your sails. You also become familiar with the vessel that will be part of your new lifelong adventure. A sailboat can seem daunting with all its moving parts, but it is quite simple.
I recently learned the term Keel Hauling, and I was a bit shocked at not knowing the reference. When you sail, you take on an entirely new language of words, sayings, and jargon. A few of us sailors even embrace the same Jimmy Buffet songs as part of our perennial sailing playlist. (that is another story for a different time)
My wife, who has sailed for over 20 years, is competent under most conditions at sail and knows her way around our vessel, but I was surprised that she didn’t know some of the simple terms that we sailors use daily. There are some fundamental terms that all sailors learn as they begin their sailing career and the rest of the information follows along as you spend more time on the water.
When you embark on a sailing education in ASA 101 Basic Keelboat Sailing, you learn about the anatomy of a boat. These are part of the fundamentals of sailing. While these few terms are interchangeable among boats, they certainly are not the only terms you’ll learn, but they are the beginning of a new language when you become an ASA certified sailor.

This is a keelboat. It is different from a dinghy in that it is larger than 20 feet and has a keel. Keelboats start at around 20 feet with no upper limit in length. A 200-foot megayacht is considered a keelboat.
Sailboat Terminology

Dinghy – A small sailboat usually under 20 feet long and open for most of its length.

Keel – A fixed appendage on the bottom of the hull that provides sideways resistance needed to counter the force of the wind on the sails. The keel also carries ballast , usually iron or lead, the weight of which counteracts the force of the wind that causes a sailboat to heel , or lean over.
Hull – The watertight structural shell of a boat.
Bow – The forward part of a boat
Stern – The aft part of the boat.
Transom – The more or less flat surface that closes the hull at the stern
Rudder – The sailboat is steered by a fin-shaped appendage attached beneath the boat toward the stern which can be rotated to change the angle at which the water strikes it. Water must flow past the rudder in order fo rit to work so it will not turn the boat while at rest.
The rudder is controlled by a wheel or a tiller at the helm of the boat. The person steering the boat is the helmsman .
Cockpit – The area of the boat, usually recessed into the deck , from which the boat is steered and sailed.
Deck – The generally horizontal surface that encloses the top of the hull.
Companionway – The entrance from the cockpit or deck to the cabin.
Stanchion – A metal post that supports lifelines .
Lifeline – A wire supported on stanchions around the perimeter of the deck to prevent crew from falling overboard.
Pulpit – A guardrail at the bow or stern of a boat to which (usually) the lifelines are connected.
Learning to Sail
- ASA 101: What You’ll Learn ASA 101 is your introduction to Basic Keelboat Sailboat and is your key to a lifetime of sailing.
- How To Sail Sailing a boat is part art and part skill but few activities offer such a variety of pleasures as sailing. Something special occurs when you cast off the lines and leave your cares at the dock.
- 7 Tips For The Beginning Sailor There are the obvious things you need when you go sailing, sunscreen, a hat, a windbreaker, non-skid shoes, and wind. However, what do you really need to be ready to head out on the water?
- How To Learn To Sail You won’t have to buy a boat or learn a new language or buy a new wardrobe to get a taste for sailing. You can dictate how much you want to experience.
- Learning To Sail Is Just The Beginning Sailing means different things to different people. At ASA we understand that learning to sail is just the beginning of a relationship with a lifestyle that is infectious. Where will sailing take you? We have a few ideas but how you view sailing is the most important.
- What Is Your Role on a Boat? What type of sailor are you and what role do you take on the boat? Your ASA sailing education will prepare you to be a skipper on a sailing vessel and with that comes the responsibility of keeping your crew safe and ensuring the safety of the vessel you are sailing.
Related Posts:

- Learn To Sail
- Mobile Apps
- Online Courses
- Upcoming Courses
- Sailor Resources
- ASA Log Book
- Bite Sized Lessons
- Knots Made Easy
- Catamaran Challenge
- Sailing Vacations
- Sailing Cruises
- Charter Resources
- International Proficiency Certificate
- Find A Charter
- All Articles
- Sailing Tips
- Sailing Terms
- Destinations
- Environmental
- Initiatives
- Instructor Resources
- Become An Instructor
- Become An ASA School
- Member / Instructor Login
- Affiliate Login

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Racing Terms and Phrases for Newer Sailors. The angle between the apparent wind and the chord line of the sail. The direction and speed of the wind as measured from a moving boat. Tacking away from other boats to obtain clear air. Often used for starting situations.
The tack (or gybe) that lets you sail the most distance without getting to the layline. Sail the long tack first is a strategy rule of thumb. 1) The leading edge of a sail 2) Heading up toward the wind (luffing up) 3) The bubbling or fluttering of a sail when sailing too close to the wind. A less skilled sailor.
Reach - sailing perpendicular to the wind, at an angle between a beat and a run. Run - sailing downwind away from the windward mark. Start line - the line across which boats start a race. Starting gun - the signal that starts the race. OCS - "on course side," meaning a boat crossed the start line too early and must restart.
The pre-start is an important part of a sailboat race. It is a time sequence where boats jockey for position and attempt to win the start. It employs many of the devices, rules and tactics that are involved in sailboat racing in a short amount of time. Over early penalty If a boat crosses the line early there is a two-boat length penalty.
The Beginnings of a Basic Sailboat Racing Glossary. We make our sport harder to understand than it should be. The combination of actual technical terms and slang can be an imposing barrier to those trying to get into sailboat racing.All too often I forget and start casually slinging around terms that make my editors go "huh?"
boat through the wind. Head to wind: When the bow of the boat points into the wind. Head up: To sail closer to the wind. Heel : The way a boat tips to one side as it sails. Helmsman/Helm: The person who steers the boat. Hike: To use crew weight to keep the boat flat by leaning out. Hull: The body of the boat.
major sailing news, commentary, opinions, features and dock talk . . . with a North American focus. ... Racing Terms: Glossary for newer sailors. Published on September 5th, 2021
A term used in yacht racing to indicate the speed of a sailboat towards (or from) the direction of the wind. 'Fly Time' The amount of time the boat spends foiling. The ideal situation would be for a team to make it around the entire course with 100 percent fly time, which means their hull never touches the water. 'Wingwash'
Here are the key sailing terms you'll want to know as you begin learning to sail! Port: Facing forward, this is anything to the left of the boat. When you're onboard, you can use this term pretty much any time you would normally say "left.". Starboard: Facing forward, this is anything to the right of the boat.
Trapeze: To stand on the side of the boat to maximize the effect of the body weight. Trim: To adjust the sail to the right shape and angle to the wind. The process of "hiking out," or changing the center of gravity of the boat in order to go faster. Upwind: Toward the direction from which the wind blows; windward.
From the salty whispers of old seadogs to the crisp commands on a racing skiff, mastering these 30 essential sailing terms will transform you from a landlubber to a savvy sailor. Hoist the sails and let's navigate the nautical jargon together! Must-Know Sailing Terms, Phrases and Slang: Aft. Beam.
Racing a sailboat is a lot of fun. It blends the excitement of sailing your own boat with the raw rivalry of trying to beat another boat of comparable size. Racing also teaches you boat handling and sail trim in a manner that cruising cannot: by comparing your speed and handling to those of other boats. Let us jump into the article to learn ...
Close-Hauled. Sailing as close to the wind as possible, with the sail set at a sharp angle to the boat. Beam Reach. Sailing perpendicular to the wind, with the sail set at a right angle to the boat. Broad Reach. Sailing with the wind at a diagonal angle behind the boat, with the sail angled away from the boat. Running.
Dead downwind - Sailing in a direction straight downwind. Deck - The mostly flat area on top of the boat. De-power - Reducing the power in the sails by luffing, easing the sheets, or stalling. Dinghy - A small sailboat or rowboat. Displacement - The weight of the boat; therefore the amount of water that it displaces.
The combination of actual technical terms and slang can be an imposing barrier to those trying to get into sailboat racing. All too often I forget and start casually slinging around terms that make my editors go "huh?" So, we thought we would start Racer's Edge 2024 off with a primer on frequently used terms from the race course.
Draft. Boat's draft is the distance from the water surface to the deepest point of the boat. In other words, the draft is the minimum water depth you can go to and not scrape your hull or keel. Better double this number when sailing, just to be safe, as hitting the seabed can have disastrous consequences.
June 17, 2024. Sailboats are powered by sails using the force of the wind. They are also referred to as sailing dinghies, boats, and yachts, depending on their size. Sailboats range in size, from lightweight dinghies like the Optimist dinghy (7'9") all the way up to mega yachts over 200 feet long. The length is often abbreviated as LOA (length ...
40 terms to help you start talking like a sailor. Aft - The rear section of the boat. Bow - The front section of the boat. Mast - The vertical pole that supports the sails. Boom - The horizontal pole that extends from the mast and supports the foot of the mainsail. Winch - A device used to adjust the tension on a rope or wire, usually ...
Beam: The widest part of a boat. 8. Berth: The bed on a boat; also a slip in a marina. 9. Bilge: The lowest part of a boat's interior hull. 10. Binnacle: A casing on the deck that holds the ship's compass. 11. Boom: The horizontal pole extending from the mast to hold the bottom of a sail.
Hull. The hull is the main body of the sailboat, providing buoyancy and stability in the water. It's typically made of fiberglass, wood, or metal, and its shape and design can vary depending on the type of sailboat. The hull is divided into several sections, including the bow (front), stern (rear), port (left side), and starboard (right side).
Kellhauling - As a form of punishment, to be dragged through the water under the keel either at the beam or from bow to stern. A severe naval punishment during the 15th and 16th centuries. The victim, presumably a delinquent sailor, was dragged from one side of the boat to the other, under the bottom of the boat (keel).
Excerpt from Dock Talk blogspot: "SAILORSPEAK" a new book by Bob Roitblat does a good job of summarizing some of the commonly used terms into one easy reference book. Bob has been racing in the Beneteau First 36.7 fleet aboard Steve Pelke's "Stingray " and has recently undertaken being an author. "SS" is his first entry into being ...
Sailboat Terminology. Dinghy - A small sailboat usually under 20 feet long and open for most of its length. ... Winning Tactics Around the Race Course In this online class series, elevate your racing game with champion sail racer Dave Perry. Ideal for sailors of all levels, we'll learn boat-on-boat tactics and strategic maneuvers for ...